Table 2.
Simulation for settings without any HTE present
| Normal | Gumbel | Std-Gamma | T-mixture | Cox-PH | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Censoring | SE | ME | SE | ME | SE | ME | SE | ME | SE | ME |
| 200 | none | 0.000 | 0.095 | 0.000 | 0.040 | 0.000 | 0.070 | 0.000 | 0.060 | 0.000 | 0.140 |
| 200 | light | 0.000 | 0.095 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.075 | 0.350 | 0.000 | 0.380 | 0.000 | 0.015 |
| 200 | heavy | 0.000 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.055 | 0.000 | 0.290 |
| 1000 | none | 0.000 | 0.803 | 0.073 | 2.066 | 0.092 | 1.483 | 0.161 | 3.087 | 0.176 | 3.824 |
| 1000 | light | 0.061 | 1.989 | 0.015 | 0.967 | 0.213 | 2.674 | 0.066 | 3.176 | 0.111 | 3.405 |
| 1000 | heavy | 0.002 | 1.253 | 0.000 | 0.484 | 0.030 | 1.176 | 0.123 | 2.953 | 0.135 | 2.688 |
Results are based on 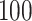 simulation replications. Average
percentage of patients exhibiting strong evidence (SE) of
differential treatment effect (i.e.
simulation replications. Average
percentage of patients exhibiting strong evidence (SE) of
differential treatment effect (i.e. 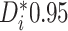 )
and average percentage of patients exhibiting mild evidence (ME) of
differential treatment effect (i.e.
)
and average percentage of patients exhibiting mild evidence (ME) of
differential treatment effect (i.e. 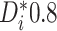 ).
Results are shown for AFT models with the same four residual distributions used in
the simulations from Section 4.1 and for a
Cox-proportional hazards model with no treatment-covariate interactions. Censoring
levels were varied according to: none, light censoring (
).
Results are shown for AFT models with the same four residual distributions used in
the simulations from Section 4.1 and for a
Cox-proportional hazards model with no treatment-covariate interactions. Censoring
levels were varied according to: none, light censoring (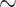
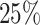 of
cases censored), and heavy censoring (
of
cases censored), and heavy censoring (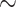
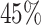 of
cases censored).
of
cases censored).
