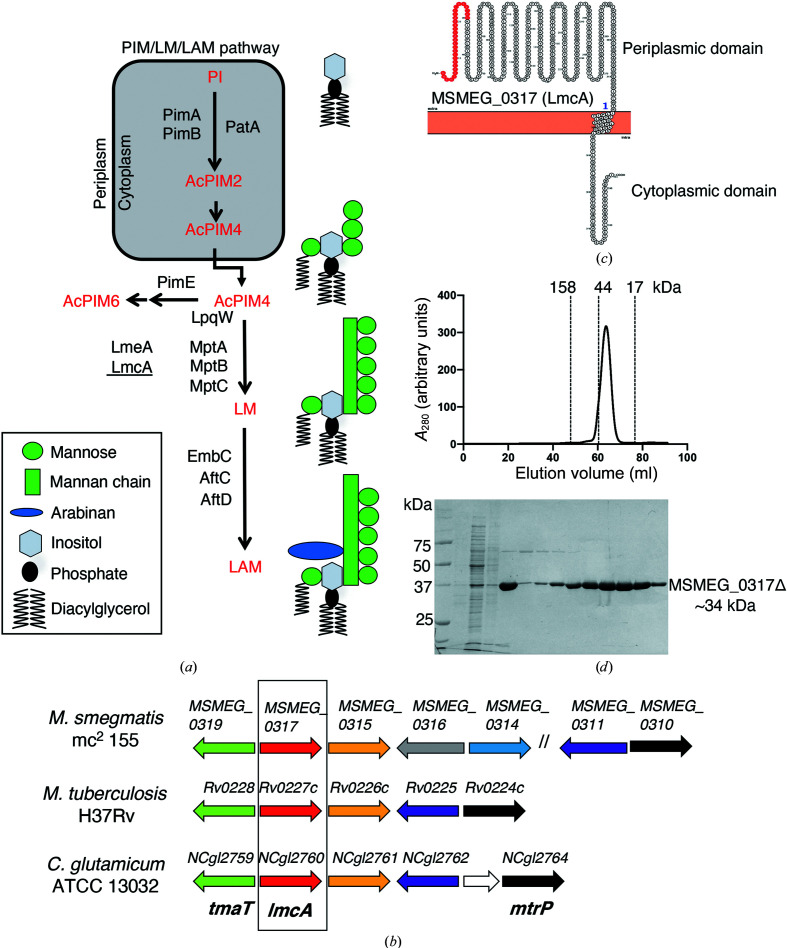
Figure 1.
(a) The PIM/LM/LAM biosynthetic pathway of mycobacteria. Early steps of PIM synthesis are performed by the cytoplasmic enzymes PimA (Korduláková et al., 2002 ▸), PimB (Guerin et al., 2009 ▸; Lea-Smith et al., 2008 ▸) and PatA (Korduláková et al., 2003 ▸) to produce AcPIM2 from phosphatidylinositol (PI). Further mannosylation yields AcPIM4, which is transported to the periplasm and can be processed by the mannosyltransferase PimE (Morita et al., 2006 ▸) to form AcPIM6, an end product, or channelled into a parallel pathway for LM and LAM synthesis by the lipoprotein LpqW (Crellin et al., 2008 ▸; Kovacevic et al., 2006 ▸; Marland et al., 2006 ▸). LM/LAM synthesis is catalysed by the PPM-dependent mannosyltransferases MptB, MptA and MptC (Kaur et al., 2006 ▸, 2007 ▸; Mishra et al., 2007 ▸, 2008 ▸; Mishra, Krumbach et al., 2011 ▸). A phospholipid-binding protein, LmeA (Rahlwes et al., 2017 ▸), is involved in maintaining MptA under stress conditions (Rahlwes et al., 2020 ▸). The focus of the current study, LmcA (underlined), also functions at the MptA step in C. glutamicum (Cashmore et al., 2017 ▸). (b) The MSMEG_0317 genetic locus. The MSMEG_0317 gene is encoded within a locus that is highly conserved in Corynebacterineae. Likely orthologous genes in the three species are shown using the same colour. Previously studied genes are tmaT (Yamaryo-Botte et al., 2015 ▸) and mtrP (Rainczuk et al., 2020 ▸), both with roles in cell-wall mycolic acid transport, and the LM/LAM biosynthesis gene NCgl2760 (Cashmore et al., 2017 ▸), while the remaining genes are uncharacterized. The focus of the current study is boxed. (c) Predicted membrane topology of MSMEG_0317. Following cleavage of the putative signal peptide (red), the mature protein is proposed to comprise a large periplasmic N-terminal domain, a single transmembrane domain and a small cytoplasmic tail. (d) The elution profile of MSMEG_0317Δ on a HiLoad 16/60 Superdex 75 gel-filtration column suggesting a monomeric protein (top) and SDS–PAGE analysis of the eluted MSMEG_0317Δ (∼34 kDa) (bottom). The molecular-weight markers used for calibration are bovine γ-globulin (158 kDa), chicken ovalbumin (44 kDa) and equine myoglobin (17 kDa). See also Supplementary Fig. S1.