Fig. 4.
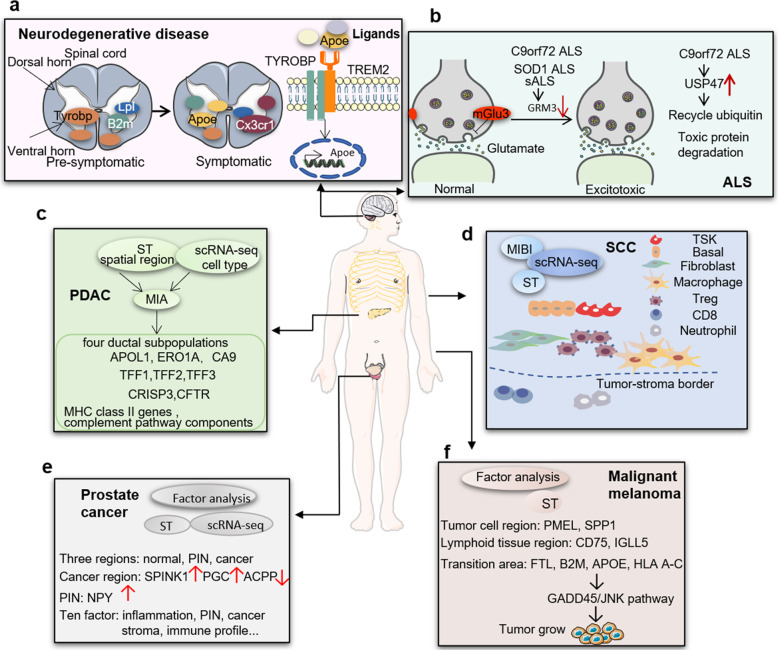
Spatial transcriptomics provide new insights for understanding molecular mechanisms of human diseases and preclinical disease models. a In neurodegenerative disease models, Trem2 and Tyrobp form a receptor complex that can trigger phagocytosis or regulate cytokine signaling, when bound by membrane lipids or lipoprotein complexes. Tyrobp expression is up-regulated before symptoms and before Trem2 expression in the ventral horn and white matter. Lp1 and B2m are up-regulated before symptoms, especially in the ventral horn. Apoe and Cx3cr1 are up-regulated in the spinal cord of symptomatic mice. Apoe expression is driven by Trem2 signal and the ligand of Trem2. b In amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) models, expression of GRM3 gene in the prefrontal lobe and motor cortex was lower in C9orf72 repeat expansion, mutant SOD1, and sALS. The GRM3 gene encodes mGlu3, a metabotropic glutamate receptor, regulates the neurotransmission of glutamate in the central nervous system. The expression of neuronal mGlu3 receptor is mainly at presynaptic terminals. When the extrasynaptic glutamate overflows excessively, the G protein signaling cascade is activated to regulate the activity of presynaptic ion channels, followed by negatively regulating the release of presynaptic glutamate. The regulation that the decrease of mGlu3 receptor expression in the prefrontal cortex increases the transmission of glutamate and produces excitotoxicity may be a common mechanism feature between schizophrenia and ALS. c Spatial positions of different subgroups are identified and mapped within cell type in the entire tissue by integrating scRNA-seq and MIA. A total of four ductal subgroups are identified, including ductal population, terminal ductal population, centroacinar duct population, and antigen-presenting duct cells, respectively expressing APOL1, ERO1A and CA9 genes; TFF1, TFF2 and TFF3; CRISP3 genes; CD74, HLA -DPA1, HLA-DQA2, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DRB5, and C1S, C4A, C4B, CFB and CFH genes. d The combined application of spatial transcriptomics, scRNA-seq, and MIBI demonstrates that TSK cells and basal tumor cells are located on the leading edge. Fibroblasts, macrophages and Tregs are most abundant at the tumor-stroma boundary, while CD8 T cells and neutrophils are largely excluded from the tumor, indicating that the localization of Tregs may prevent effector lymphocytes into the tumor. e The gene expression in 3 regions obtained by factor analysis is applied for identifying region-specific markers in normal, cancer and PIN region. Enrichment of SPINK1 and PGC, the depletion of ACPP, and the increase of NPY level in the PIN area are observed in cancer areas. In addition, the interaction between factors was determined by hierarchical clustering of ten factors. These ten factors include normal glands signature, normal glands, stroma, inflammation, PIN, cancer, immune profile, proximity to PIN signature, and mix of prostatic atrophy and stroma et al. f In malignant melanoma models, PMEL and SPP1 overexpressed in tumor cell clusters, and the lymphoid tissue regions from and adjacent to tumor cell regions were characterized by the expression of immune-related genes CD74 and IGLL5, respectively. FTL, B2M, APOE and HLA-related genes (HLA A-C) express in the transition zone and related to tumor growth regulation through the GADD45/JNK pathway