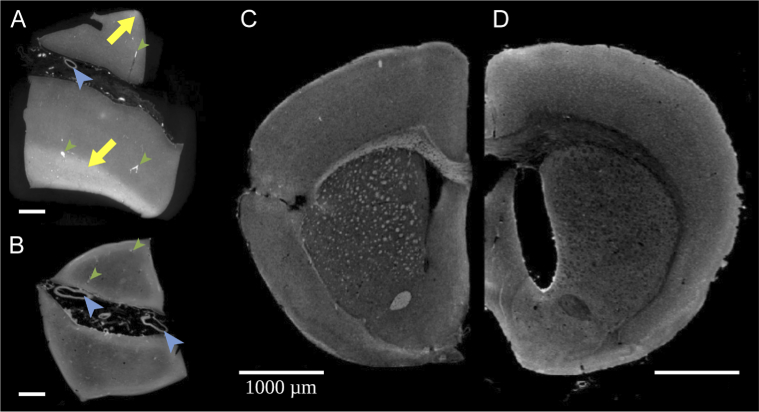
Fig. 3.
White matter fiber tracts are revealed by XPCT in a human brain and disappear upon demyelination brain clearing. (A-B) Single XPCT slice of a human brain sample from 2 distinct but adjacent blocks. (A) Ethanol dehydration reveals white matter as hyperintense areas (arrows); (B) White matter hyperintense signal is lost after demyelination by brain clearing. Other anatomical landmarks such as large vessels are clearly seen (large blue arrowheads). Because the sample was not perfused, there is also contrast from small vessels (smaller green arrowheads); (C-D) Single XPCT slice through a rodent brain (C) without and (D) with demyelination by brain clearing: note the disappearance of white matter hyperintense signal. Clearing procedure induced brain expansion and ethanol dehydration induced brain shrinkage, hence the slight difference in sample size.