Figure 2.
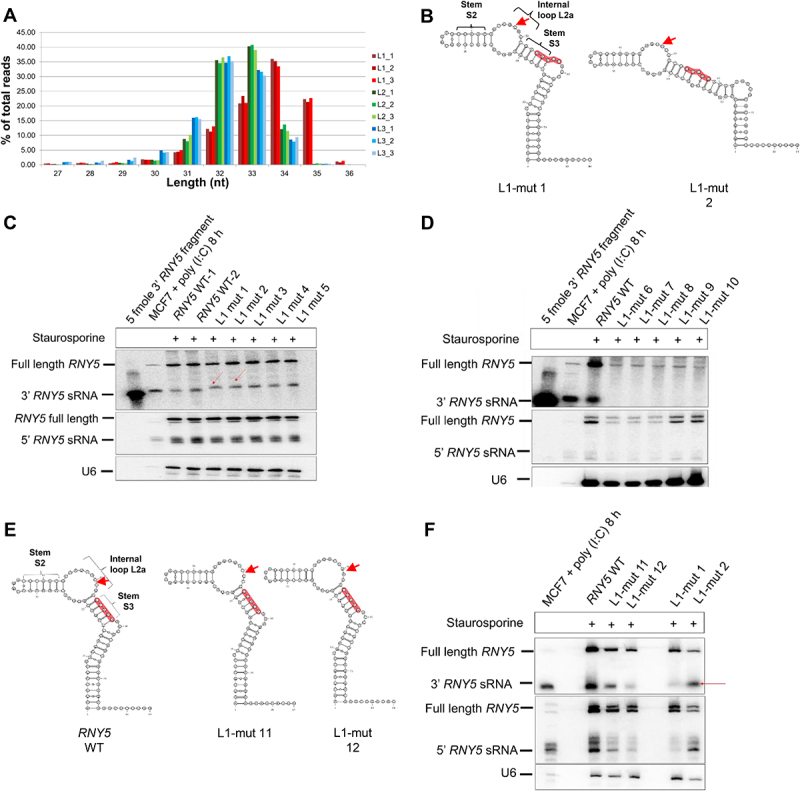
3’ end ysRNA production is Y RNA structure dependent. L1 mutants generate longer ysRNAs when compared to L2/L3 mutants. (A) Total read percentage for each cDNA library replicate of L1/L2/L3 mutant pools at each size ranging from 25–34 nts. L2/L3 mutant derived ysRNAs (green and blue) are mainly 32/33 nt. L1 mutant derived ysRNA reads (red) are longer with a length of 34/35 nt. (B) Predicted structures of the two most abundant L1 RNY5 mutants generate longer ysRNA reads compared to wild type RNY5. (C) Most abundant L1 RNY5 mutants generate longer ysRNAs compared to wild type RNY5. (D) Northern blot of the least abundant L1 RNY5 mutants shows no ysRNAs. (E) L1 RNY5 mutants with the same predicted structure as wild type generate wild type sized ysRNAs. Apart from the L1 RNY5 mutants that fold the same way as wild type RNY5 the structural features of wild type RNY5 including the stem S, internal loop L2a and stem S3 close to the 3’ end cleavage site are shown. (F) L1 RNY5 with the same structure than wild type RNY5 produce wild type sized ysRNAs.
