Figure 4.
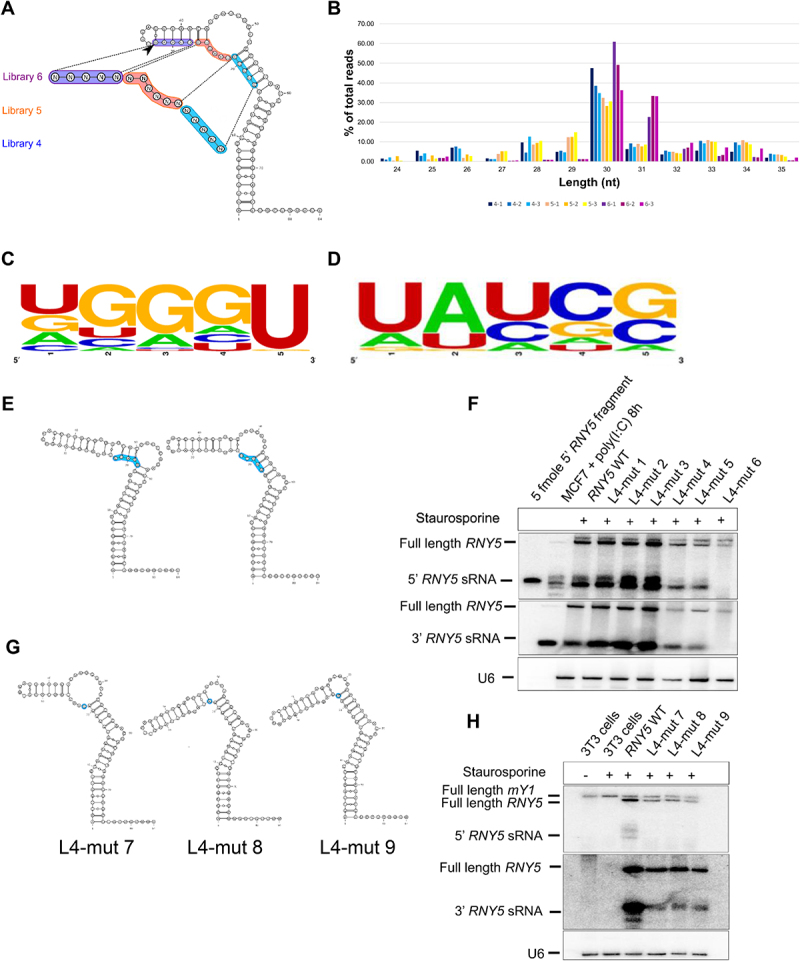
5’ end Y RNA cleavage is UGGGU sequence dependent. (A) Structure of wild type human RNY5 including the three mutant pool regions that were selected for 5’ end mutagenesis analysis. In each of the regions of mutant pool L4 (blue), L5 (Orange) and L3 (purple) near the 5’ end cleavage site (indicated with an arrow between positions 32 and 33) 5 nt substitution mutations were introduced resulting in 1,024 possible combinations for each library. (B) L4/L5 mutants produced mainly 30 nt ysRNAs whereas L6 mutants produced mainly 30/31 nt ysRNAs. (C) Sequence logo analysis showed a strong selection for the wild type RNY5 sequence motif UGGGU. (D) Sequence logo analysis showed that for all abundant L5 produced ysRNAs there was strong selection for the first three positions to be UAU. (E) Predicted L4 RNY5 mutants fold similar to wild type RNY5 and the two most abundant L4 RNY5 mutants are shown as representatives. (F) L4 RNY5 mutants generate wild type sized ysRNAs. (G) Predicted RNY5 mutant structures with mutations at position 22. U was replaced by A, C and G. (H) Y RNA cleavage was affected at the 5’ end of RNY5 if the U at position 22 of RNY5 was mutated.
