Figure 4.
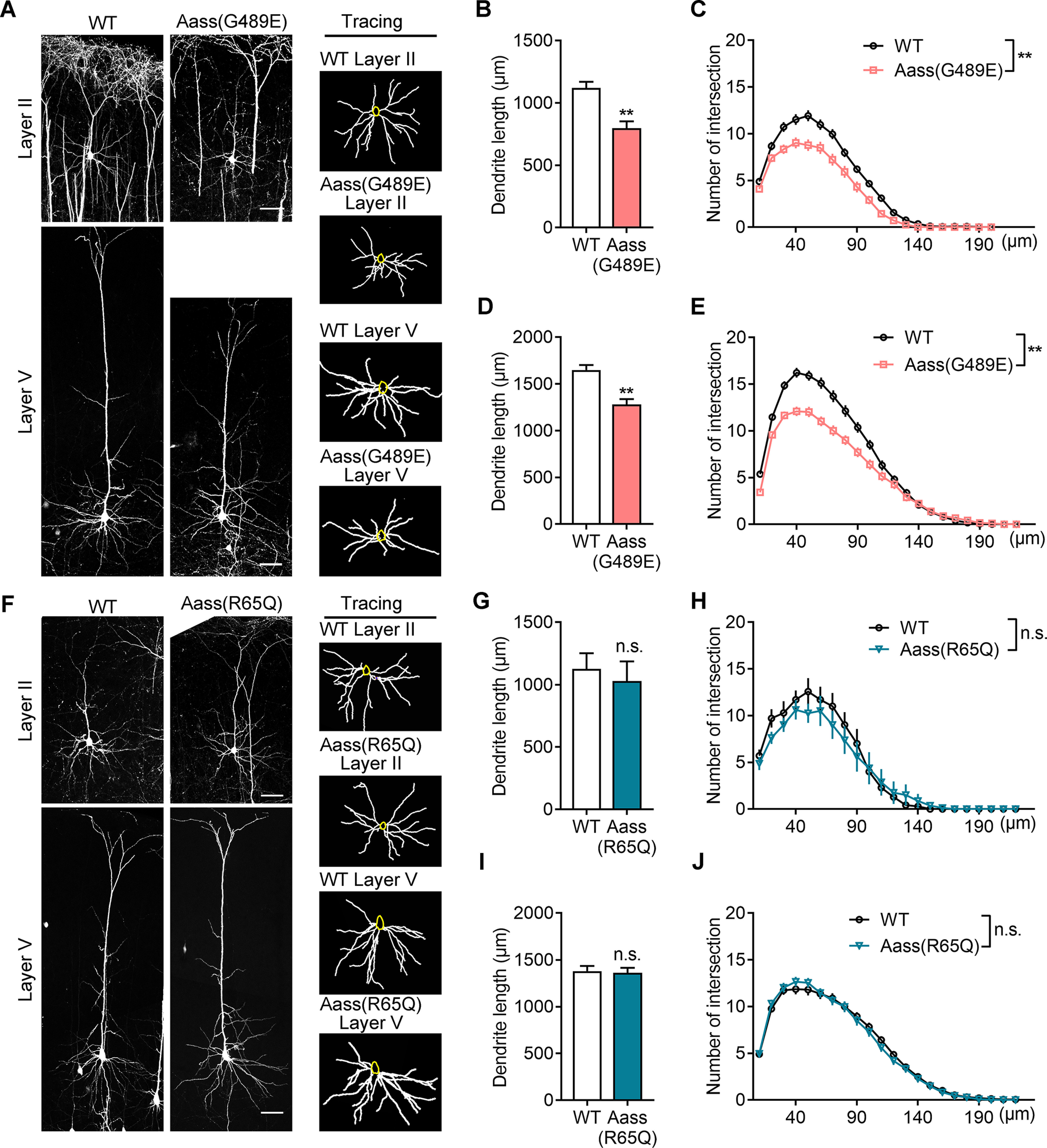
SDH mutation, but not LKR mutation, leads to impaired dendritic development. A, Representative images (left) of Thy1-GFP-labeled pyramidal neurons in Layer II and Layer V of WT, Aass (G489E) somatosensory cortex at P42. The basal dendrites of pyramidal neurons were reconstructed using the ImageJ software (right). Scale bars: 50 μm. B, C, Quantification of the total basal dendritic length (B, Student's t test, **p = 0.0066) and the basal dendritic complexity (C, univariate ANOVA, F(1,5) = 18.442, **p = 0.008) of Layer II pyramidal neurons in A. WT, 51 neurons, n = 4 brains; Aass (G489E), 43 neurons, n = 3 brains. D, E, Quantification of the total basal dendritic length (D, Student's t test, **p = 0.0057) and the basal dendritic complexity (E, univariate ANOVA, F(1,6) = 15.863, **p = 0.007) of Layer V pyramidal neurons in A. WT, 41 neurons, n = 4 brains; Aass (G489E), 44 neurons, n = 4 brains. F, Representative images (left) of Thy1-GFP-labeled pyramidal neurons in Layer II and Layer V of WT, Aass (R65Q) somatosensory cortex at P42. The basal dendrites of pyramidal neurons were reconstructed using the ImageJ software (right). Scale bars: 50 μm. G, H, Quantification of the total basal dendritic length (G, Student's t test, p = 0.1124) and the basal dendritic complexity (H, univariate ANOVA, F(1,5) = 4.139, p = 0.098) of Layer II pyramidal neurons in F. WT, 53 neurons, n = 4 brains; Aass (R65Q), 38 neurons, n = 3 brains. I, J, Quantification of the total basal dendritic length (I, Student's t test, p = 0.7302) and the basal dendritic complexity (J, univariate ANOVA, F(1,5) = 0.125, p = 0.783) of Layer V pyramidal neurons in F. WT, 47 neurons, n = 4 brains; Aass (R65Q), 41 neurons, n = 3 brains. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n.s., no significance, p > 0.05, **p < 0.01.
