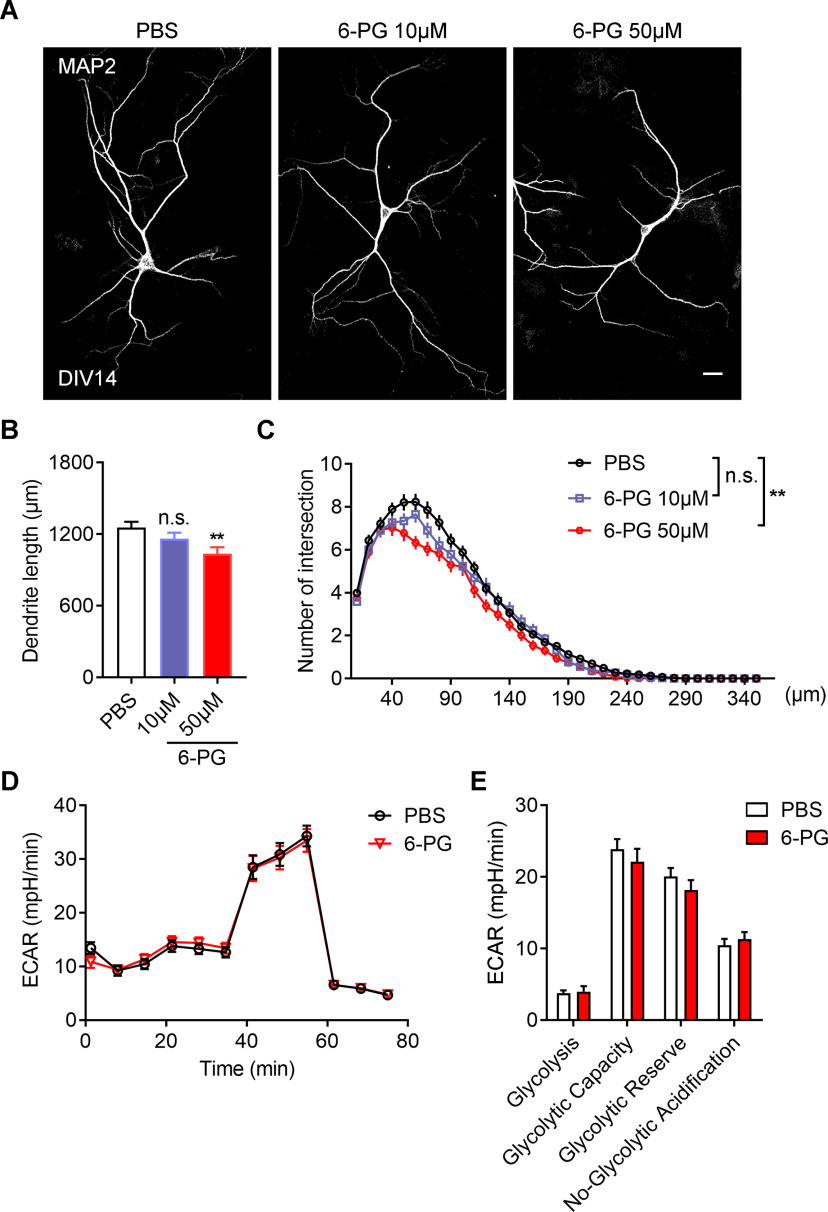
Figure 9.
Inhibition of extracellular function of GPI impairs neuronal development without affecting glycolysis. A, Representative images of primary neurons dissected from WT brains. The neurons treated with or without 6PG in different concentrations as indicated from DIV4 to DIV14 and stained with MAP2 antibodies at DIV14. Scale bars: 20 μm. B, C, Quantitative analysis of the total basal dendritic length (B, one-way ANOVA, F(2,6) = 0.2276; PBS vs 6PG 10 μm, p = 0.0999; PBS vs 6PG 50 μm, **p = 0.0037) and the basal dendritic complexity (C, univariate ANOVA, PBS vs 6PG 10 μm, F(1,4) = 3.946, p = 0.118; PBS vs 6PG 50 μm, F(1,4) = 29.193, **p = 0.006) of cultured neurons in (A). PBS, 96 neurons; 6PG 10 μm, 63 neurons; 6PG 50 μm, neurons; n = 3 independent experiments. D, E, Representative profile of glycolysis stress assay (D) showing the ECAR of the cultured neurons treated with or without 6PG (50 μm). Graph in E showing glycolysis, glycolytic capacity, glycolytic reserve and nonglycolytic acidification of neurons in D. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n.s., no significance, p > 0.05, **p < 0.01.