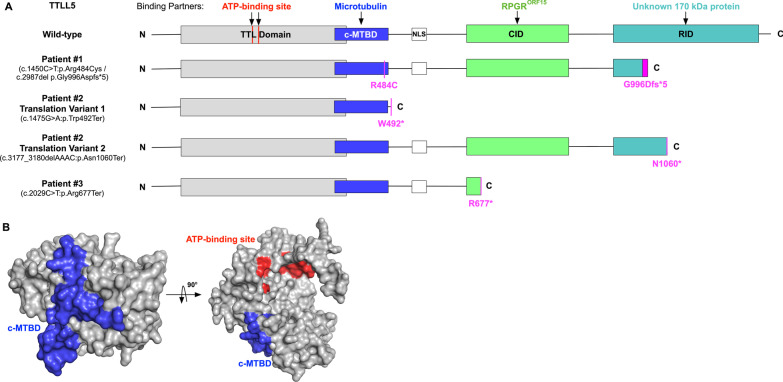
Fig. 7.
Structural modeling of TTLL5 domain shows mutants disrupt interactions with binding partners. The domain topology of wild-type TTLL5 and patient mutants are illustrated (A). The TTL domain is shown in the grey box, the c-MTBD is shown in the blue box, the nuclear localization signal region is shown in the white box, the CID is shown in the green box, and the RID is shown in the magenta box. The ligands and their corresponding binding domains are indicated with arrows. Each patient mutation is shown in magenta. The homology-based model of the TTLL5 TTL domain is demonstrated in a surface model (B). The ATP-binding site is highlighted in red, and the microtubulin-binding site is highlighted in blue