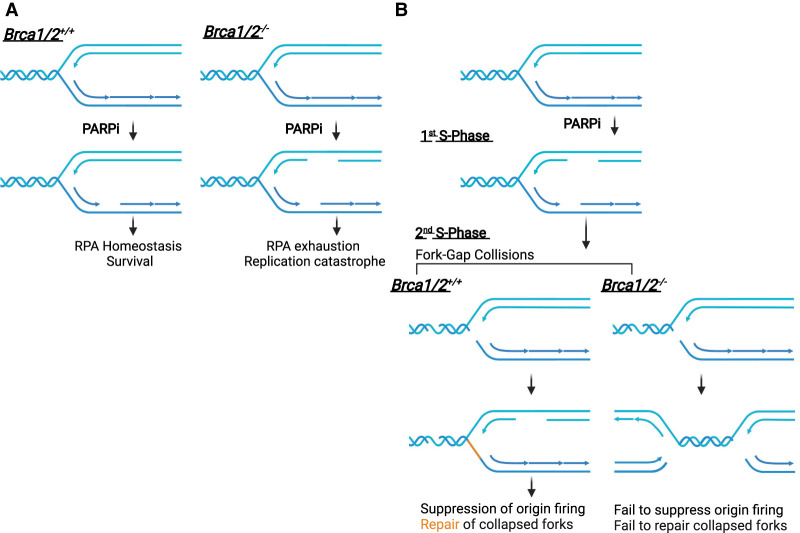
Figure 3.
Models for the selective killing of BRCA1/2-deficient cells by PARPi. (A) PARPi induces more ssDNA gaps in BRCA1/2-deficient cells, promoting RPA exhaustion and replication catastrophe. (B) PARPi induces ssDNA gaps during replication and prevents complete gap repair, allowing gaps to persist into the next cell cycle and generate DSBs upon collisions with replication forks. BRCA1/2-deficient cells fail to repair collapsed forks and mount a checkpoint response, leading to progressive accumulation of DSBs over multiple cell cycles and cell death.