Fig. 3.
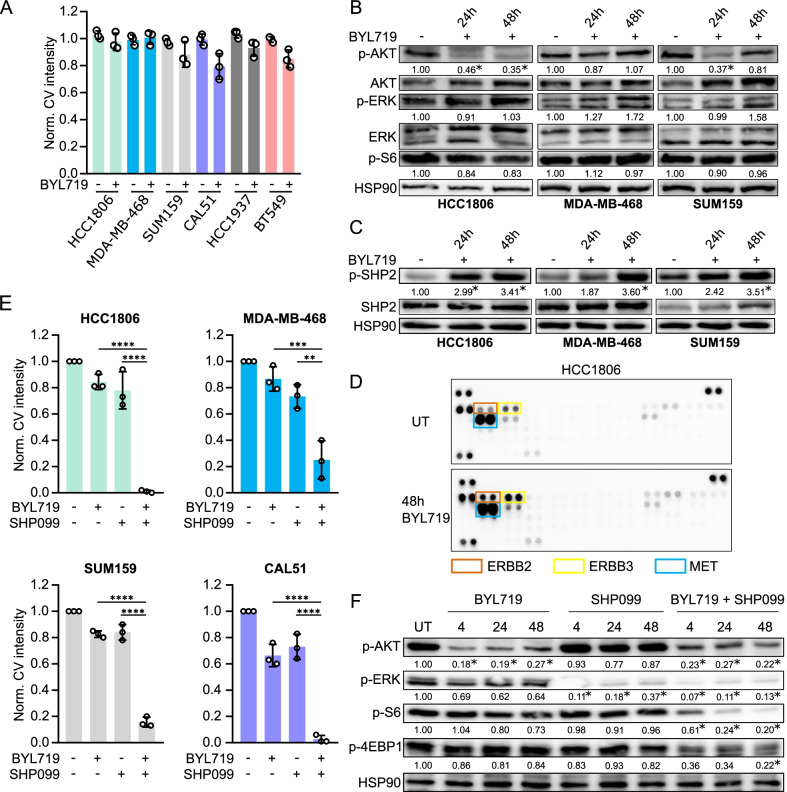
Targeting SHP2 effectively combats intrinsic resistance to PI3K inhibitor in TNBC cells. a A panel of PI3K inhibitor-resistant TNBC cell lines treated with BYL719. Quantification of crystal violet staining intensity of three independent colony formation experiments is shown. BYL719: 5 μM (HCC1806, MDA-MB-468, HCC1937, BT549), 2 μM (CAL-51, SUM159). b Western blot showing the biochemical effects on PI3K and MAPK signaling upon BYL719 treatment in HCC1806 (5 μM), MDA-MB-468 (5 μM) and SUM159 (2 μM) cells. Significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) in signaling in comparison to the untreated condition are marked with an *. c BYL719 treatment induces phosphorylation of SHP2 on residue Y542 in HCC1806 (5 μM BYL719), MDA-MB-468 (5 μM) and SUM159 (2 μM) cells. Significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) in induction of SHP2 phosphorylation in comparison to the untreated condition are marked with an *. d RTK arraying of HCC1806 cells treated with 5 μM BYL719 for 48 h reveals activation of several RTKs. e BYL719/SHP099 combination treatment in HCC1806, MDA-MB-468, SUM159 and CAL51 cells prevents resistance to BYL719. Quantifications of crystal violet staining intensity of three independent colony formation experiments. Significance between indicated conditions was calculated by one-way ANOVA. **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001. BYL719: 5 μM (HCC1806, MDA-MB-468), 2 μM (SUM159, CAL51). SHP099: 10 μM (HCC1806), 15 μM (SUM159), 20 μM (MDA-MB-468, CAL51). f PI3K and MAPK signaling is abrogated in HCC1806 cells that are treated with the combination of BYL719 and SHP099. BYL719: 5 μM. SHP099: 10 μM. Significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) in signaling in comparison to the untreated condition are marked with an *