Fig. 4.
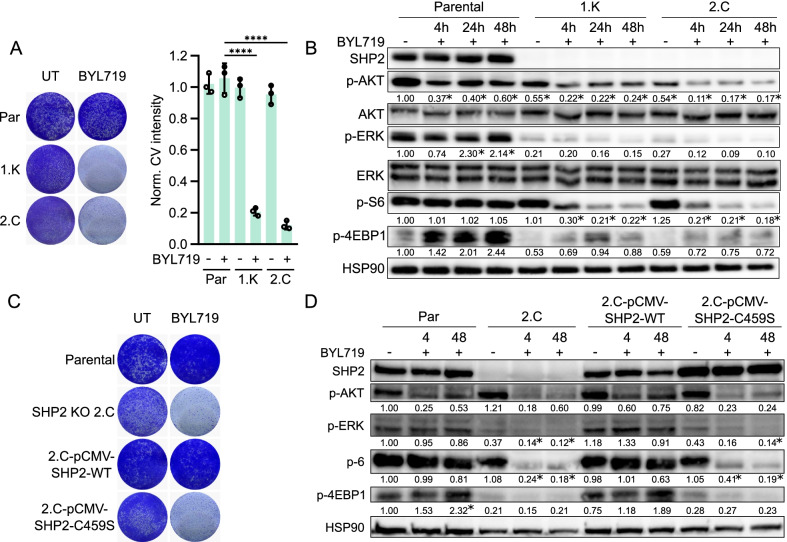
The phosphatase SHP2 is indispensable for mediating BYL719 resistance in TNBC cells. a Left: Colony formation with HCC1806 parental cells and two independent SHP2 knockout clones treated with 5 μM BYL719. Right: crystal violet intensity quantification of three experiments. Significance between indicated conditions was calculated by one-way ANOVA. ****p ≤ 0.0001. b Western blot analysis showing the biochemical effects on PI3K and MAPK signaling in HCC1806 parental versus SHP2 knockout cells after 5 μM BYL719 treatment. Significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) in signaling in comparison to the untreated condition in parental cells are marked with an *. c Colony formation with HCC1806 SHP2 knockout clone 2.C, reconstituted with either wild type SHP2 (pCMV-SHP2-WT) or a phosphatase-dead mutant (pCMV-SHP2-C459S), treated with 5 μM BYL719. HCC1806 parental and 2.C cells serve as controls. d Biochemical effects on PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways in HCC1806 parental, SHP2 KO 2.C and in wild type SHP2 and phosphatase-dead SHP2 reconstituted cells after treatment with 5 μM BYL719. Significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) in signaling in comparison to the untreated condition in parental cells are marked with an *