Table 2.
Modification of plant N-glycan by glycoengineering to make protein compatible for functioning in humans
| S/N | Amino Acid | Glycomoeity | Enzymes involved | Resultants Glycostructure | Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | -ASN- |
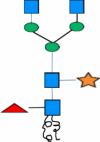
|
Xylosyltranferases&fucosyltransferases (Genetic knock-out) |

|
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)-derived immunoglobulins (IgGs) was produced in plants which do not show any difference in Enzyme-link immunosorbent specificity assay | [82, 83] |
| B | -ASN- |

|
Galactosyltransferases |
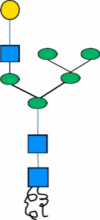
|
Production of recombinant immunoglobulin which does not serve as a substrate for plant specific xylose and fucose | [74] |
| C | -ASN- |

|
β1,4-galactosyltranferases |
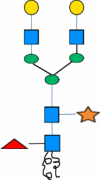
|
Production of antibody similar to the one produced by hybridoma technology | [76, 84] |
| D | -ASN- |

|
β1,4-galactosyltransferase with RNAi of fucosyl- and xylosyltranferases |
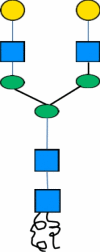
|
Production of human-compatible antibody | [84] |
| E | -ASN- |
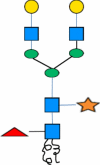
|
Xylosyl and fucosyltransferases, β1,4-galactosyltransferase, & α2,6-sialyltransferase |

|
Introduced sialic acid to the plant-derived proteins | [80] |
| F | -ASN- |

|
α1,3-fucosyltransferase and β1,4-galactosyltransferase |

|
protected galactosylated N-glycans from endogenous plant β-galactosidase activity | [85] |
