Figure 1.
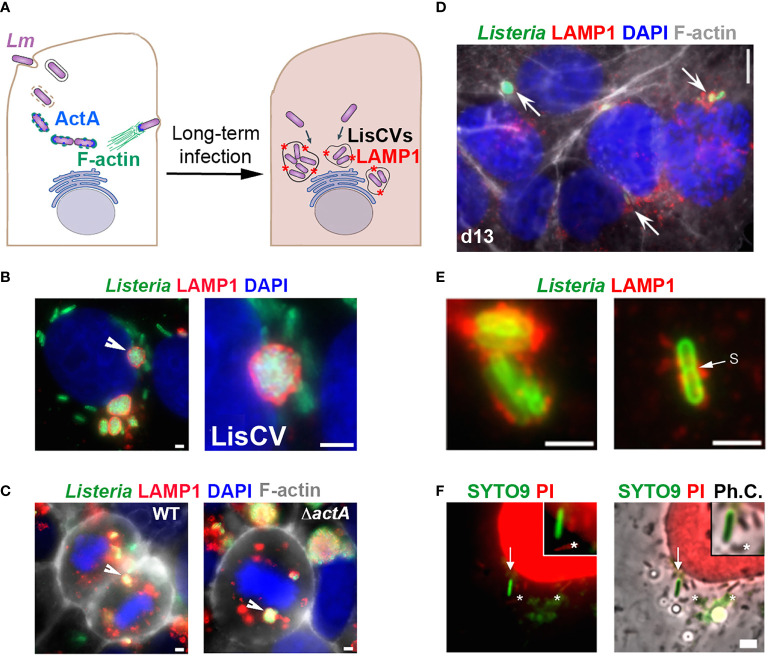
Evidence for an intracellular VBNC state of L. monocytogenes (adapted from (Kortebi et al., 2017). (A) Simplified diagram of the different phases of the intracellular life of Lm in epithelial cells. Bacteria are internalized into the host cell and are contained in an entry vacuole. After escape into the cytosol, bacteria multiply and produce ActA, which allows them to polymerize actin (F-actin), move into the infected cell, and spread to adjacent cells (not shown). After a few days of infection, cytosolic bacteria cease to produce ActA and are captured in membrane compartments, forming Listeria-containing vacuoles (LisCVs) marked with LAMP1 (represented by red stars). In these acidic vacuoles, a subpopulation of bacteria can resist degradation and multiply slowly, up to entry into dormancy. (B, C) Observation of LisCVs by epifluorescence microscopy in human placental JEG3 cells infected for 3 days with Lm. LisCVs labelled with LAMP1 are in red, Listeria in green, DNA (stained with DAPI) in blue, and F-actin in white. (B) A cell contains several perinuclear LisCVs. The arrow indicates a LisCV shown at higher magnification in the image on the right. Bars: 2 μm. (C) LisCVs are present in mitotic cells infected with either the wild-type Lm strain (WT, left) or a ΔactA mutant (right). Bars: 2 μm. White arrows indicate representative LisCVs. (D–F) Subculturing of JEG3 cells infected with ΔactA bacteria leads to VBNC bacteria. (D) Cells infected for 3 days were subcultured and propagated until day 13 (d13) and stained as in (C). Intracellular bacteria in LAMP1-positive compartments are indicated by arrows. At the same time, plating of infected cell lysates onto agar plates produces no colony (not shown). (E) High magnification images of non-culturable LAMP1-positive bacteria at d13. A bacterium with a division septum (s) is shown on the right. Bar: 5 μm. (F) JEG3 cells infected with non-culturable bacteria were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 and stained with SYTO9 and PI (see BacLight assay, Table 1 ). Intact VBNC bacteria are stained green (arrow), while damaged bacteria (*) and nuclei are stained red. “Ph.C.”: phase contrast. Bar: 1 μm. The top right squared images show higher magnifications, with one bacterium with an intact membrane (green) and three bacteria with a compromised membrane (red).