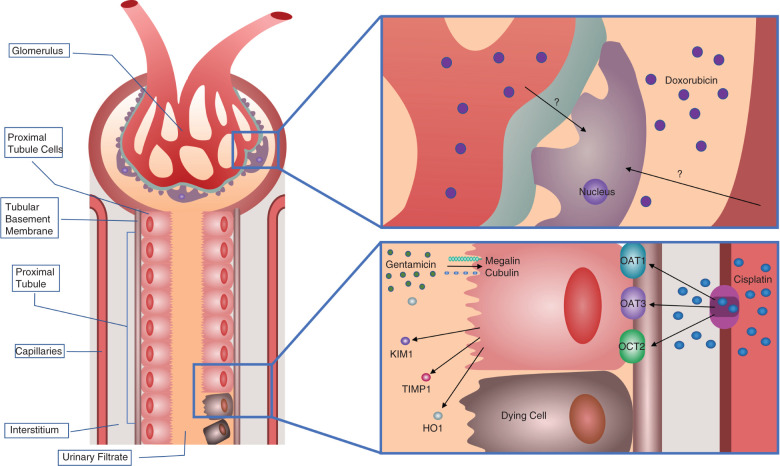
Figure 1.
Mechanism of tubular injury during AKI. Nephrotoxicants enter cells through receptor-mediated transport. For cisplatin, transport into the proximal tubule epithelial cell is facilitated by OAT1, OAT3, and OCT2 receptors on the basolateral membrane. Inflammatory and vasoactive mediators and ROS damage the tubular cells and lead to the shedding of the proximal tubule brush border, loss of polarity, and cell death by apoptosis and necrosis. Proximal tubule cell damage releases kidney injury markers, including KIM-1, NGAL, TIMP1, and HO1, into the urinary filtrate. For Dox, the transporters are unknown, but the drug induces oxidative stress resulting in podocyte apoptosis.