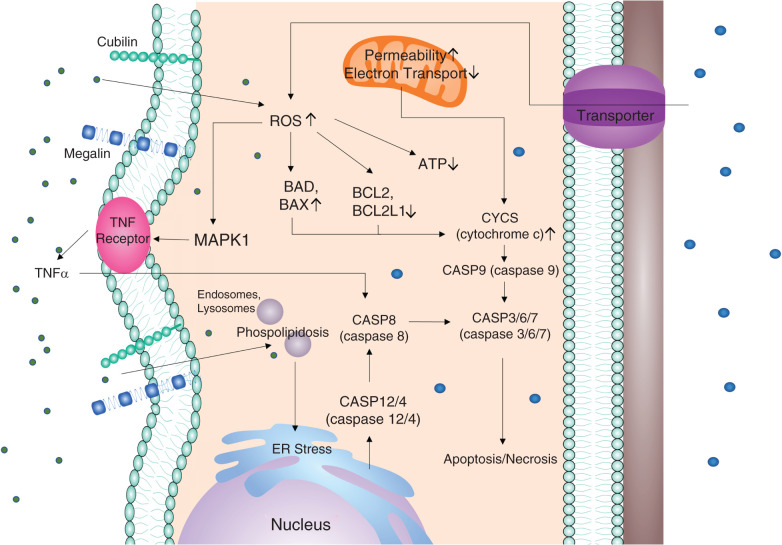
Figure 2.
Pathways of nephrotoxicant-induced tubular cell death. Nephrotoxicants enter cells through specific transporters such as OCT2 and OAT1, or endocytic renal receptors such as megalin and cubilin. The drugs damage both nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, leading to the production of ROS and subsequently activation of both mitochondrial and nonmitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and necrosis.62,129,167 Mitochondrial dysfunction activates the CASP3 cascade, leading to cell death, whereas the increase of ROS decreases levels of survival proteins such as BCL2 and increases levels of prodeath proteins such as BAX. BCL2, B-cell lymphoma 2; BAX, BCL2 associated ×.