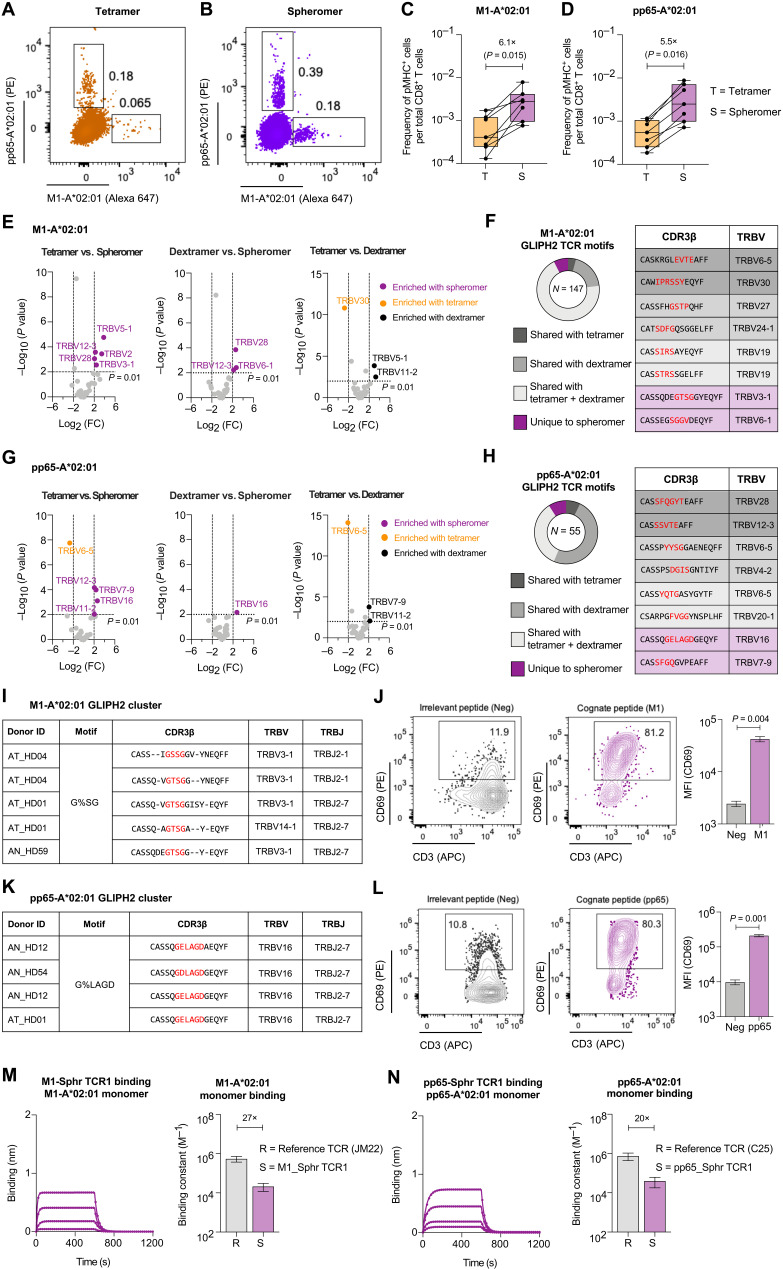
Fig. 4. Spheromer detects a higher frequency of antigen-specific T cells with a more diverse TCR repertoire.
Representative flow cytometry plots of CD8+ T cells isolated from HLA-A*02:01 individuals stained with influenza-M1 and HCMV-pp65 (A) tetramers or (B) spheromers. Enumeration of epitope-specific (C) M1 and (D) pp65 CD8+ T cells detected in healthy individuals using either tetramer or spheromer. Data from each donor (n = 7) are represented by a point. A two-tailed, matched-pairs Wilcoxon signed-rank test was performed to determine the significance levels. (E) Volcano plots showing the variance in TRBV usage of M1-A*02:01–specific CD8+ T cells detected using the spheromer and other pMHC multimers. The TRBV genes enriched significantly (P ≤ 0.01, Fisher’s exact test) are listed; the spheromers are highlighted in purple. (F) The distribution of spheromer-derived influenza-M1–specific TCR motifs identified by GLIPH2 and representative examples from each category. (G) Volcano plots representing the variance in TRBV usage of pp65-A*02:01–specific CD8+ T cells detected with distinct pMHC multimers. The TRBV genes enriched significantly (P ≤ 0.01, Fisher’s exact test) are listed; the spheromers are highlighted in purple. (H) The distribution of spheromer-derived, HCMV-pp65–specific TCR motifs identified by GLIPH2 and representative examples from each category. (I) Representative GLIPH2 cluster with specificity for influenza-M1 composed of TCR sequences identified exclusively using the spheromer. (J) Representative flow cytometry plots showing the activation of a T cell line (expressing a TCR with “G%SG” motif) stimulated with an irrelevant or cognate (influenza-M1) peptide. The activation was measured by CD69 expression. The significance level was determined by a two-tailed, paired t test. (K) Representative GLIPH2 cluster with specificity for HCMV-pp65 that is composed of spheromer-derived TCR sequences exclusively. (L) Representative flow cytometry plots showing the activation of a T cell line (expressing a TCR with “G%LAGD” motif) stimulated with an irrelevant or cognate (HCMV-pp65) peptide. The activation was measured by CD69 expression. A two-tailed, paired t test was performed to determine significance. The binding of TCR corresponding to clones from GLIPH2 clusters composed exclusively of spheromer-derived sequences to their cognate pMHC monomers (M) M1-A*02:01 and (N) pp65-A*02:01 determined by BLI. Each binding experiment was repeated at least thrice. The mean ± SD of the binding constant has been graphed and compared with a reference influenza-M1 (JM22)– and HCMV-pp65 (C25)–specific TCR.