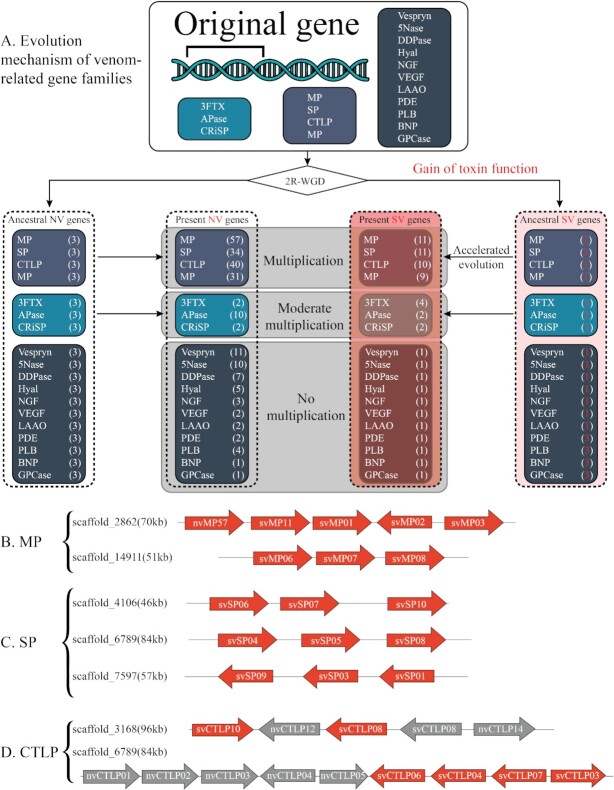
Figure 3:
Venom-related gene families in the P. flavoviridis genome. (A) Deduced evolutionary history of venom-related gene families through 2 rounds of whole-genome duplication (2R-WGD). An original set of 18 genes (shown in the top box) became 72 (4 copies each). Then, a single copy of each family was likely co-opted to develop toxic functions, resulting in 1 snake venom (SV) copy (shown in a pale red box in the right column) and 3 non-venom (NV) paralogs (shown in the see-through box to the left). (B) Tandem duplications of SVMP genes. (C) Tandem duplications of SVSP genes. (D) Tandem duplications of CTLP genes. Based on Fig. 2 and Fig. S8 from [15].