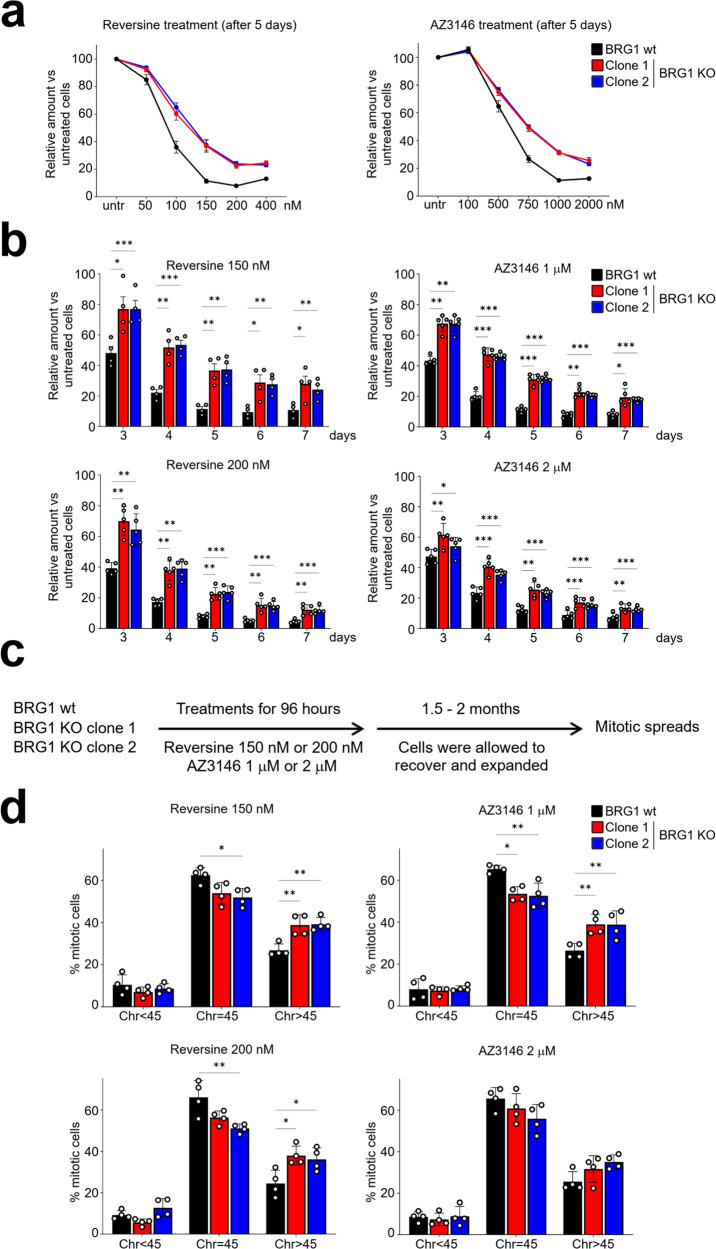
Fig. 6. BRG1-deficient cells show increased survival and aneuploidy after Mps1 inhibitor-induced chromosome missegregation.
a, b Relative cell viability in HCT116 or BRG knockout (KO) cells. Cells were exposed to the indicated concentrations of Reversine or AZ3146 for 7 days and cell viability was monitored using the sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay and normalised to untreated cell survival. Line graphs in a show the relative cell viability after 5 days of exposure to Reversine (left panel) or AZ3146 (right panel). Bar graphs in b show survival over time following exposure to 150 or 200 nM Reversine (left panels) or 1 or 2 μM AZ3146 (right panels). Data were presented as the mean ± SEM; n = 4. The p value was calculated using two-way ANOVA-Dunnett. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. c Experimental design for monitoring aneuploidy in surviving cell populations after chromosome missegregation induced by Mps1 inhibitor exposure. d Metaphase spreads prepared after treatment outlined in c were analysed, and the number of chromosomes per metaphase was quantified. The percentage of cells with chromosome gain (Chr >45), loss (Chr <45) or no change (Chr = 45) was calculated. Between 65 and 145 metaphases were analysed per sample per experiment. Data were presented as the mean ± SD; n = 4. The p value was calculated with two-way ANOVA-Dunnett assuming sphericity. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.