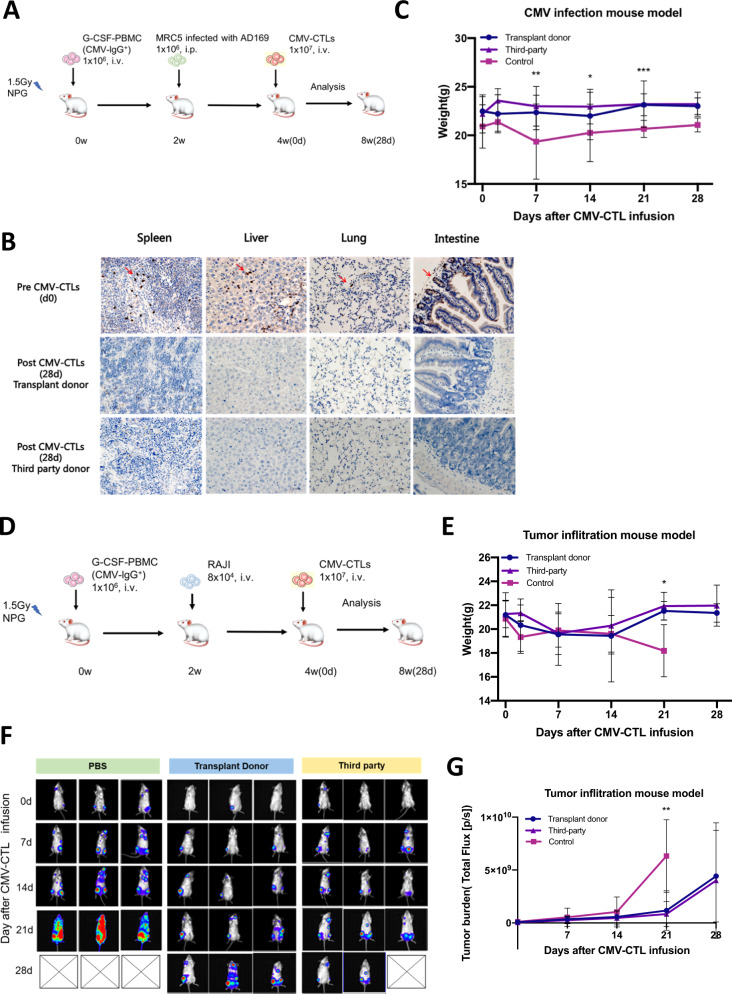
Fig. 1.
Humanized CMV infection and tumor infiltration NPG mouse models and in vivo anti-CMV efficacy. A The humanized CMV infection NPG mouse model and experimental strategy. B CMV pathology in the spleen, liver, lung, and intestine of mice pre-CMV-CTL infusion and 28 days post-donor and -third-party CMV-CTL infusion. Both donor and third-party CMV-CTLs effectively combated systemic CMV infection by diminishing CMV pathology in target organs within 28 days after CMV-CTL infusion. C Mouse weight change post-CMV-CTL infusion in the CMV infection NPG mouse model. D The humanized tumor infiltration NPG mouse model and experimental strategy. E Mouse weight change post-CMV-CTL infusion in the tumor infiltration NPG mouse model. F Photon emission and (G) tumor burden (total flux) change pre- and post-CMV-CTL infusion in the tumor infiltration NPG mouse model. No fewer than three mice were evaluated at each time point. Transplant donor and third-party CMV-CTL group vs. control group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001