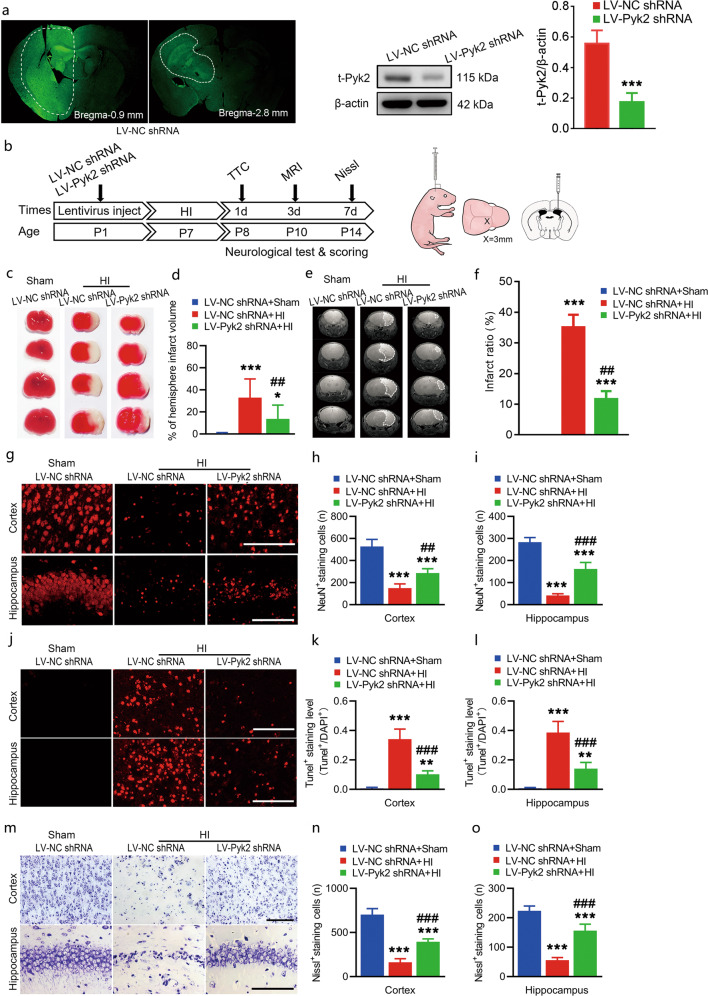
Fig. 2. Pyk2 inhibition alleviates acute brain injury after neonatal HI.
a Lentivirus infection was assessed with detecting GFP expression in vivo. The inhibition of Pyk2 was evaluated by Western blotting in tissue from the transfected region in the LV-control shRNA- and LV-Pyk2 shRNA-treated groups (n = 5/group). b Schematic of the in vivo experimental procedure and the lentivirus-injected site. c, d TTC staining was used to determine the cerebral infarction volume after HI (n = 5/group). e, f MRI imaging showing the infarct ratio on day 3 after HI (n = 10/group). g–i The survival of neurons (NeuN labeled) in the ipsilateral cerebral cortices and hippocampi of mice after HI was assessed by immunofluorescence (n = 5/group; bar = 50 μm). j–l TUNEL-positive neurons in the ipsilateral cortices and hippocampi of mice were observed 24 h after HI (n = 5/group; bar = 50 μm). m–o Nissl staining of the ipsilateral cortices and hippocampi of mice after HI (n = 5/group; bar = 50 μm). The data are presented as the means ± SD. ***P < 0.001 vs. the LV-NC shRNA group in a; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. the LV-NC shRNA + sham group in d, f, h, i, k, l, n, and o; ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 vs. the LV-NC shRNA + HI group.