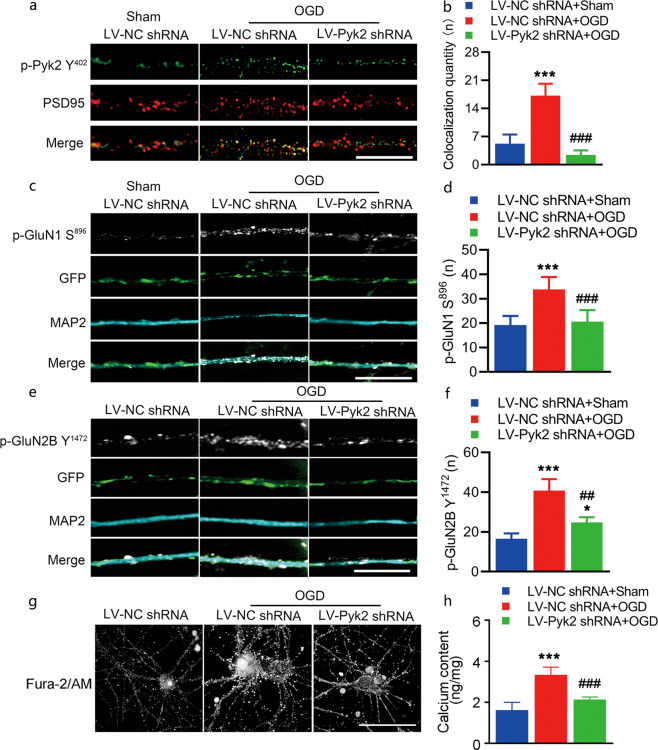
Fig. 4. Pyk2 inhibition reduces NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxic injury in vitro.
a, b Cultured cortical neurons were double stained with PSD95 and p-Pyk2 Y402 antibodies after OGD (bar = 10 μm). The colocalization of PSD95 and p-Pyk2 Y402 was quantified by counting yellow spots on axons with a length of 15 μm. Four axons from each group were included in each experiment. Data from five independent experiments were included in the analyses. p-Pyk2 Y402 was pseudocolored green. c, d Representative immunofluorescence images of NMDA receptor p-GluN1 S896 in the dendrites of cultured cortical neurons. The number of p-GluN1 S896-positive spots was increased after OGD; LV-Pyk2 shRNA pretreatment suppressed the increase in p-GluN1 S896 level after OGD (bar = 10 μm). e, f Representative immunofluorescence images of the NMDA receptor p-GluN2B Y1472 in the dendrites of cultured cortical neurons (bar = 10 μm). g A membrane-permeable calcium ion fluorescent probe was used to detect Ca2+ in neurons (bar = 5 μm). h A calcium colorimetric assay was performed. The data are presented as the means ± SD, n = 5/group. ***P < 0.001 vs. the LV-NC shRNA + sham group; ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 vs. the LV-NC shRNA + OGD group.