Fig. 1.
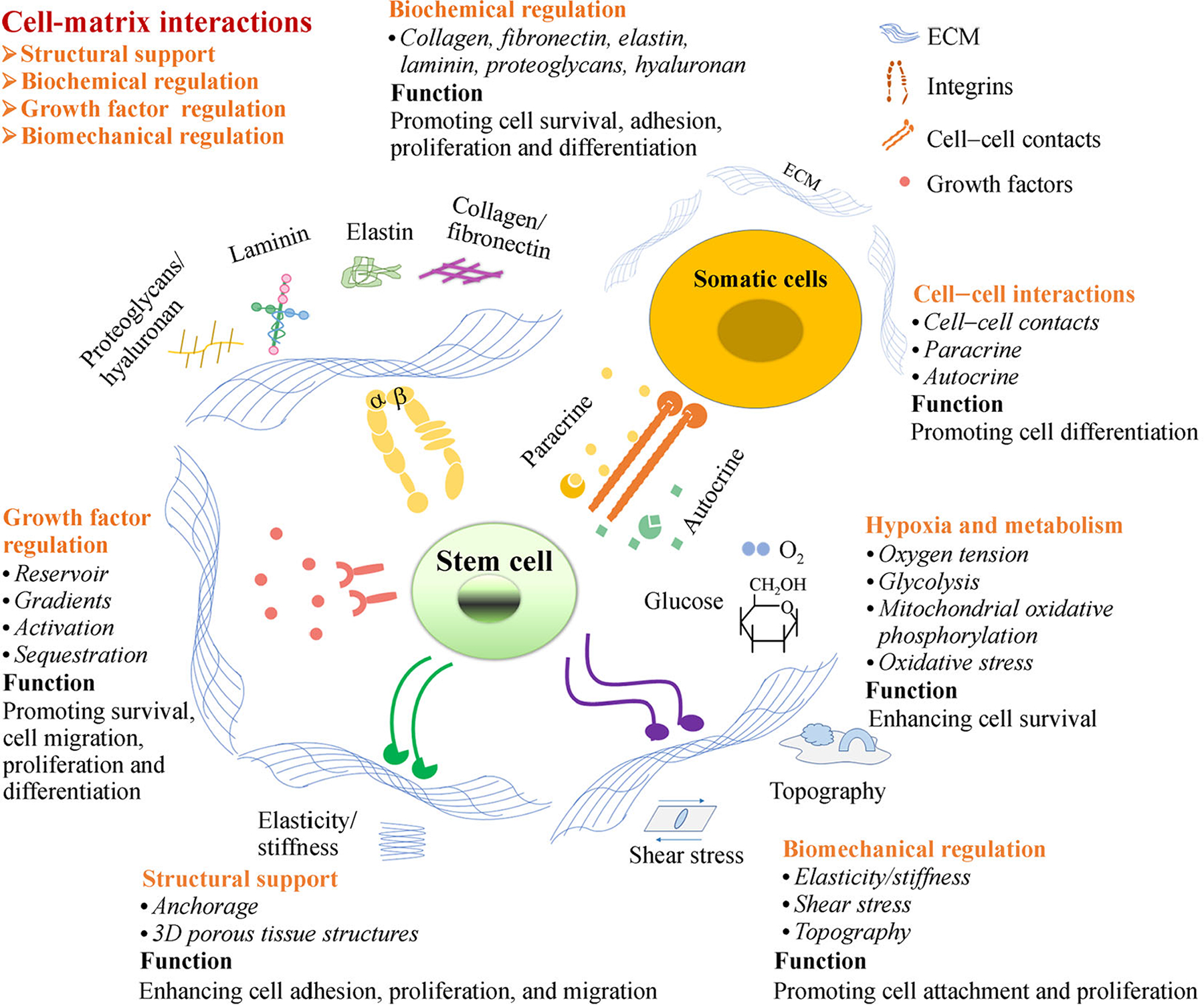
Role and composition of stem-cell niche. The stem-cell niches retain the stemness of adult stem cells in a quiescent state. When tissue is injured, the surrounding microenvironment actively signals stem cells to promote either self-renewal or differentiation to form new tissues. The niches include cell–matrix, cell–protein, protein–matrix, cell–cell interactions, hypoxia, and metabolism. Among these niche factors, cell–matrix interactions play a key role in prompting cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and differentiation for tissue regeneration. The matrix regulates stem-cell behavior through structural supports, biochemical signaling, growth factor induction, and biomechanical regulation during tissue repair.
