Fig. 4.
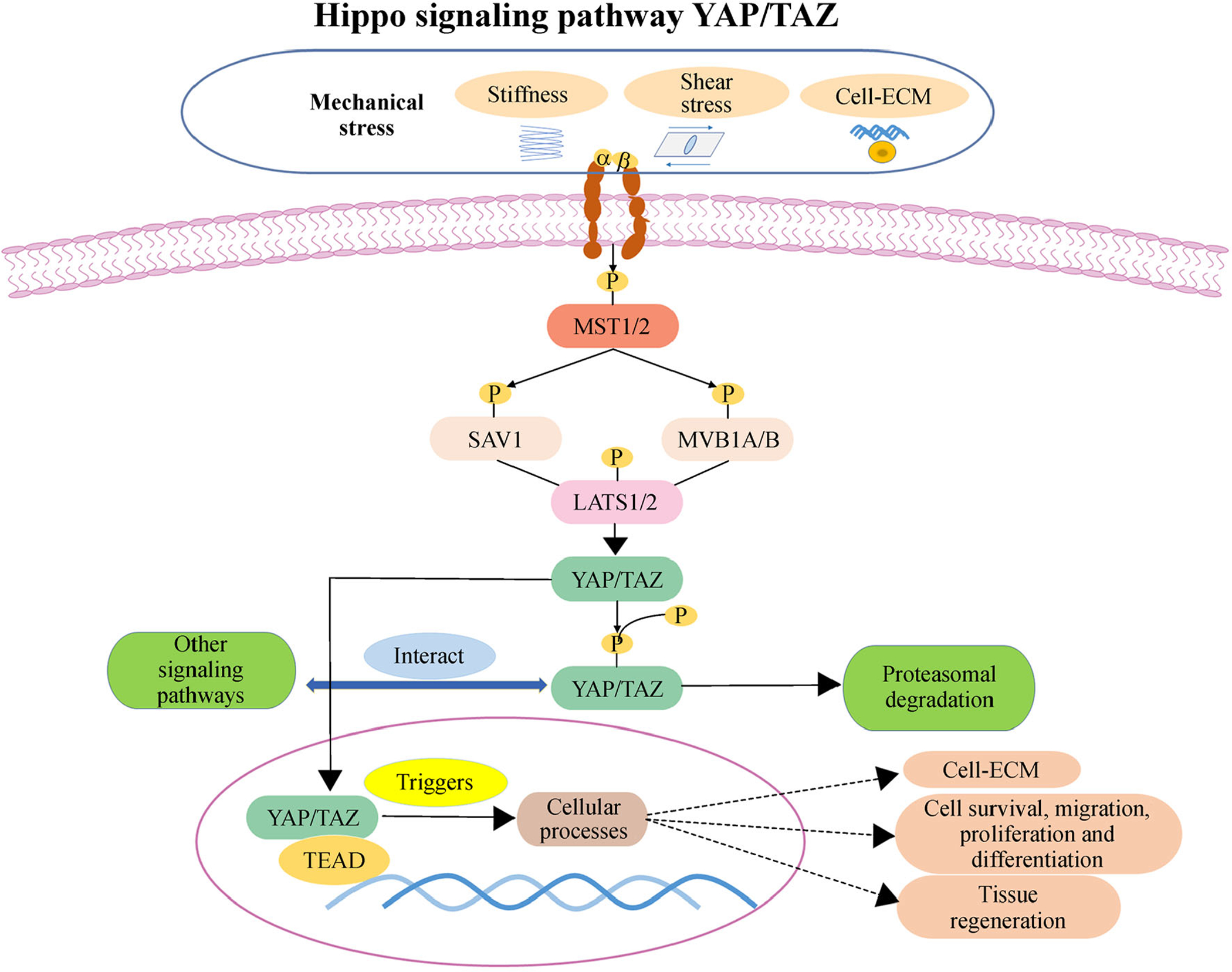
Hippo signaling pathway YAP/TAZ for regulating cell behaviors and tissue regeneration. The Hippo pathway is regulated by an intracellular network relaying a multitude of external inputs. Mechanical stress and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion changes can regulate the Hippo pathway through integrin signaling. Activation of the Hippo pathway is associated with the phosphorylation of the core Hippo pathway kinases, including mammal Ste20-like kinase 1 (MST1) and MST2, Salvador 1 (SAV1), MOB1A and MOB1B, large tumor suppressor kinase 1 (LATS1) and LATS2, the transcriptional co-activators Yes-associated protein (YAP) and transcriptional co-activator with PDZ binding motif (TAZ), which leads to proteasomal degradation. Conversely, when the Hippo kinase cascade is not activated, unphosphorylated YAP/TAZ binding with TEAD transcription factor can activate specific genes, regulating ECM remodeling, cellular behaviors (cell attachment, proliferation, migration, and differentiation) and tissue regeneration.
