FIGURE 1.
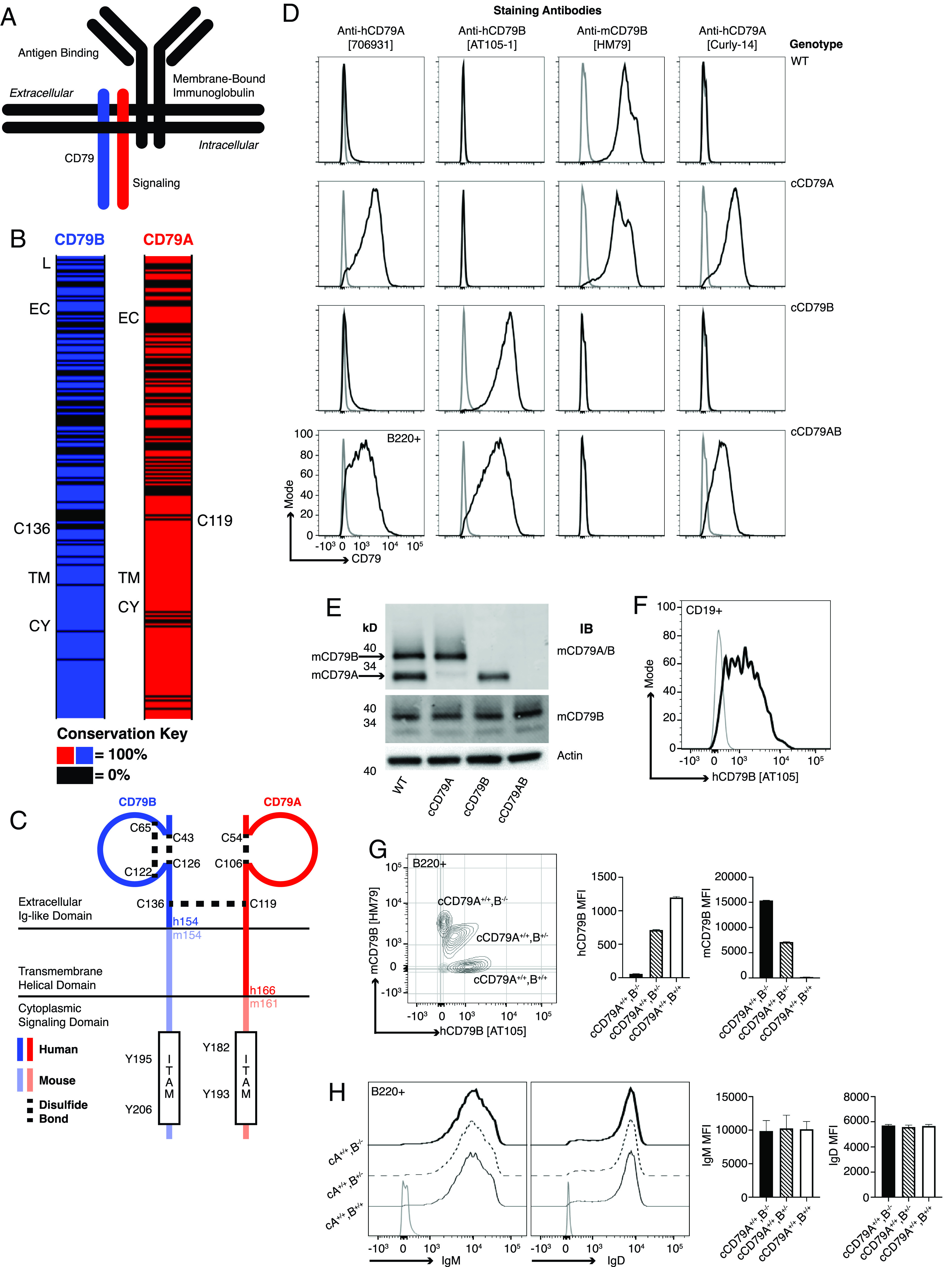
Generation of chimeric human/mouse CD79 knockin mice. (A) Schematic representation of B cell Ag receptor complex. (B) CD79 amino acid conservation between mice and humans. Black intervals represent regions of 0% amino acid conservation. Domain demarcation: CY, cytoplasmic; EC, extracellular; L, leader; TM, transmembrane. Conserved cysteines required for interchain disulfide bonding shown for each. (C) Schematic representation of cCD79. Human sequences comprise the CD79B extracellular domain and CD79A extracellular/transmembrane domains. (D) Surface staining of splenic B cells (B220+) from chimeric (h/m)CD79 knockin mice and control C57BL/6 mice. Gray lines show B220−. (E) Rabbit anti-mCD79 immunoblot analysis of whole-cell lysates (purified splenic B cells, CD43−) from cCD79 and WT mice. Upper membrane probed with a polyclonal rabbit Ab raised against a mCD79A and mCD79B extracellular domain fusion protein (Cambier laboratory). Middle membrane probed with a polyclonal rabbit Ab raised against the cytoplasmic domain of mCD79B (Cambier laboratory). An anti–β actin blot was used as a protein loading control. (F) Surface staining of B cell gated (CD19+) human PBMCs with anti-hCD79B (AT-105). Gray line shows CD19−. (G) Surface staining as a function of cCD79B allele dosage. Splenocytes from cCD79 mice of the indicated genotypes were stained with both anti-hCD79B (AT-105) and anti-mCD79B (HM79). Gray contour shows B220−. (H) IgM and IgD surface expression in chimeric mice described in (G). Gray line shows B220−. n = 4 female mice per group for (G) and (H). Error bars represent SEM. All data represent at least three independent experiments; representative data are shown.
