FIGURE 5. Intra-amniotic administration of IL-22 in mice induces lung injury and inflammation in the offspring.
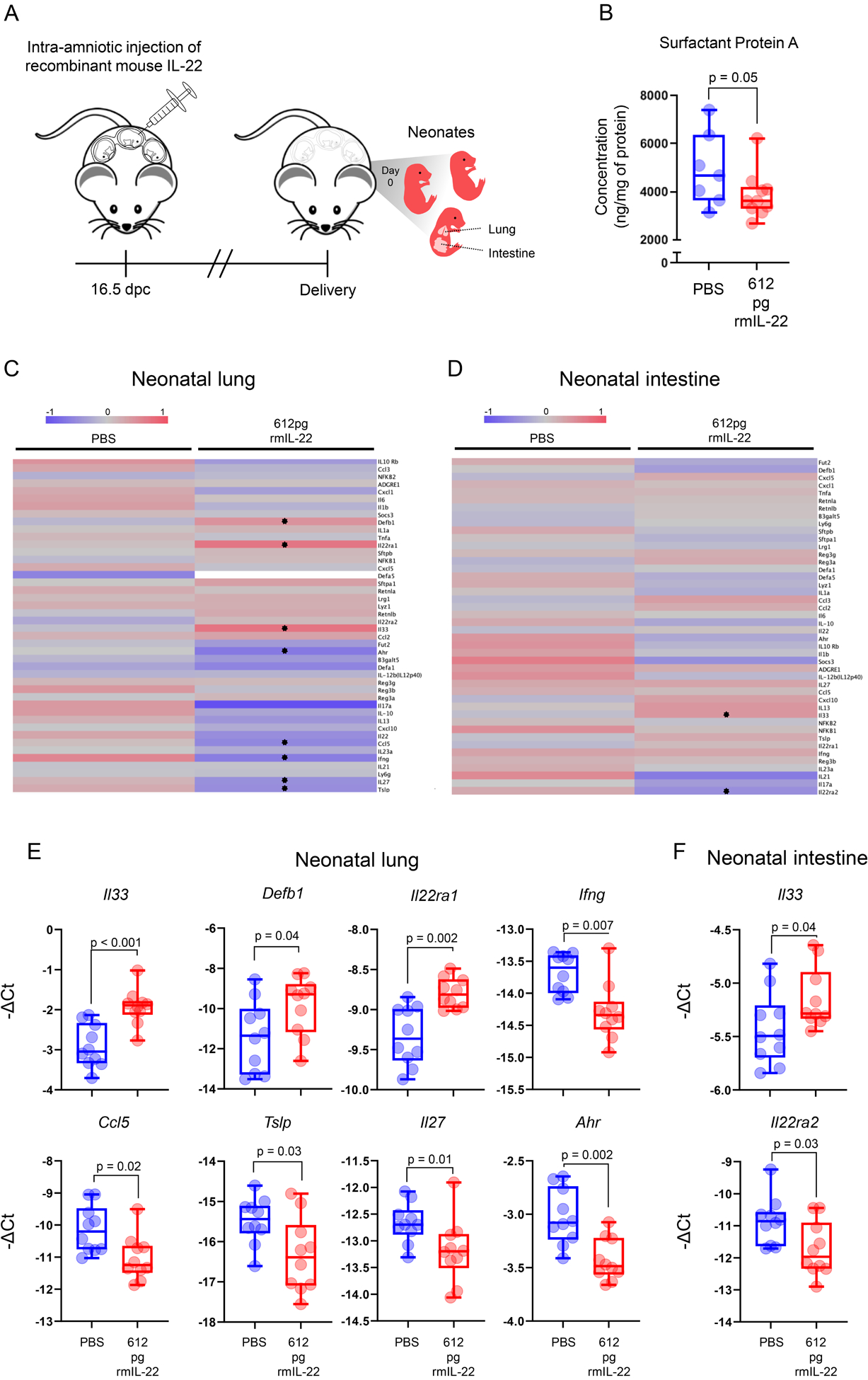
(A) Mice received an ultrasound-guided intra-amniotic injection of recombinant mouse (rm)IL-22 (612 pg/amniotic sac) (n = 10) or PBS (vehicle control; n = 7 – 10) on 16.5 days post coitum (dpc) and were monitored until delivery, after which the neonatal lung and intestine were collected. (B) Surfactant Protein A concentrations (ng/mg of protein) in the lungs of neonates born to mice intra-amniotically injected with PBS (n = 7) or rmIL-22 (n = 10). P-value was determined using a Mann-Whitney U-test. Heatmap representations showing inflammatory gene expression in the (C) lungs and (D) intestines of neonates born to mice intra-amniotically injected with PBS (n = 10) or rmIL-22 (n = 10). Red indicates upregulated expression and blue indicates downregulated expression. Stars indicate significant differentially expressed genes. (E) Expression of Il33, Defb1, Il22ra1, Ifng, Ccl5, Tslp, Il27, and Ahr and in the murine neonatal lung. (F) Expression of Il33 and Il22ra2 in the murine neonatal intestine. P-values were determined using Mann-Whitney U-tests.
