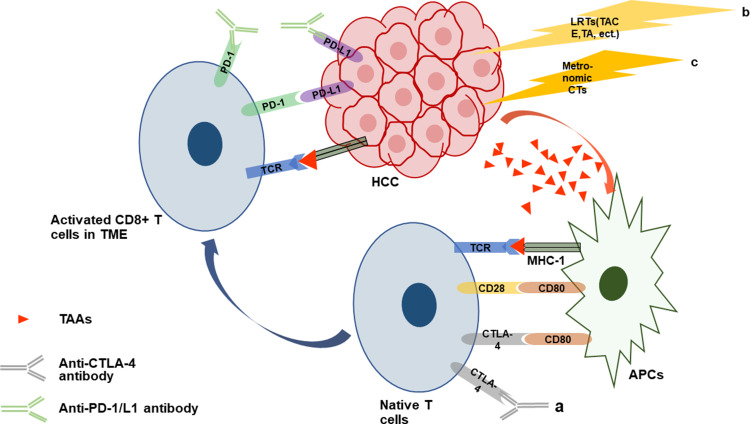
Figure 1.
Brief mechanisms of action mediating synergistic effects of combined immunotherapies. (a) Blocking the PD-1/L1 pathway alone does not induce an antitumor immune response, but inhibition of the CTLA-4 pathway via anti-CTLA-4 antibody promotes activated CD8+ T cells accumulating in lymph nodes and then infiltrating into TME, enhancing the antitumor effects of anti-PD1/L1 antibody.211 (b and c) LRTs or metronomic CTs trigger the release or exposure of immunostimulatory molecules like TAAs by damaging cancer cells, followed by the blockade of the PD-1/L1 and CTLA-4 pathway by anti-PD1/L1 and anti-CTLA-4 antibody, resulting in robust antitumor immune response229,234,246.
Abbreviations: HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; LRTs, locoregional therapies; TACE, transarterial chemoembolization; TA, thermal ablation; CTs, chemotherapies; TAAs, tumor-associated antigens; APCs, antigen-presenting cells; MHC-1, major histocompatibility complex class 1; TCR, T cell receptor; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4; TME, tumor microenvironment.