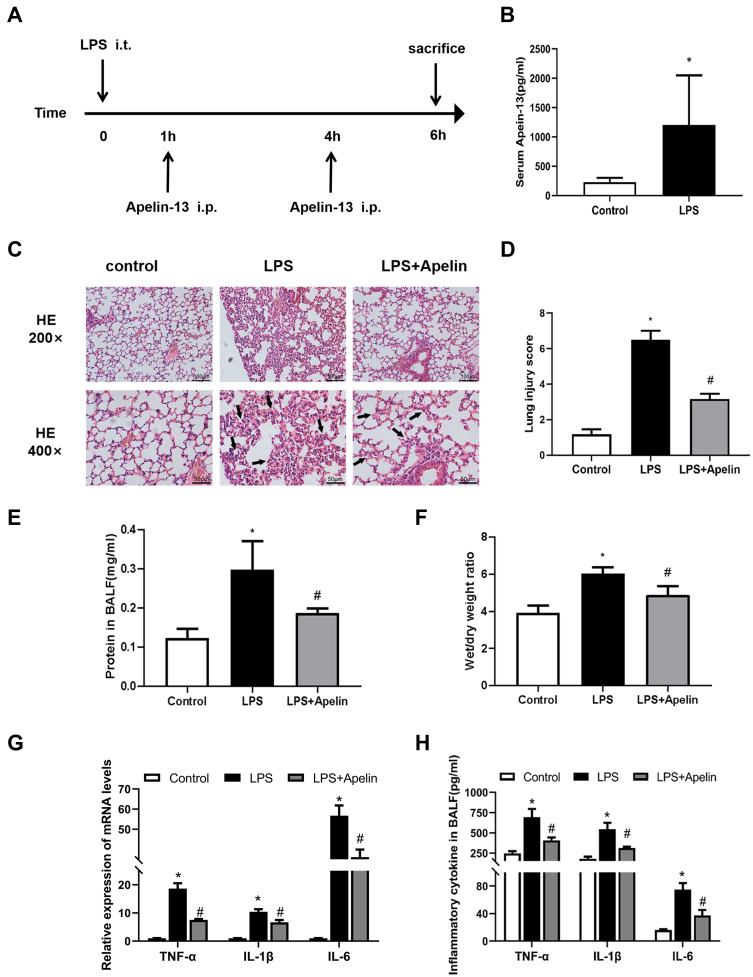
Figure 2.
Apelin-13 attenuated histological damage and lung inflammation in mice with LPS-induced lung injury. (A) The intervention dose regimen of apelin-13 in an experimental mouse model of acute lung injury. Mice were injected intraperitoneally with apelin-13 or vehicle 1 h after LPS instillation and 3 h after the initial dose of apelin-13. After 6 h of LPS instillation, the mice were killed and the tissue of lung was obtained for scheduled tests. (B) Expression of apelin-13 in the serum of the control group and the LPS treatment group. (C) Representative H&E-stained lung sections of different groups at 200x and 400 x original magnification. The alveolar walls were with intramural neutrophils (arrows). (D) Histopathological scores of different groups. (E) Total protein levels in BALF of each group. (F) The lung W/D weight ratio was assessed among experimental groups. (G) Levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in lung tissues were detected by real-time PCR. (H) Levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in BALF were detected by ELISA. Data were expressed as mean ± SD. *P<0.05 versus control group, #P<0.05 versus the LPS treatment group (n=6).
Abbreviations: LPS, lipopolysaccharide; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; W/D, wet/dry; ELISA, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6.