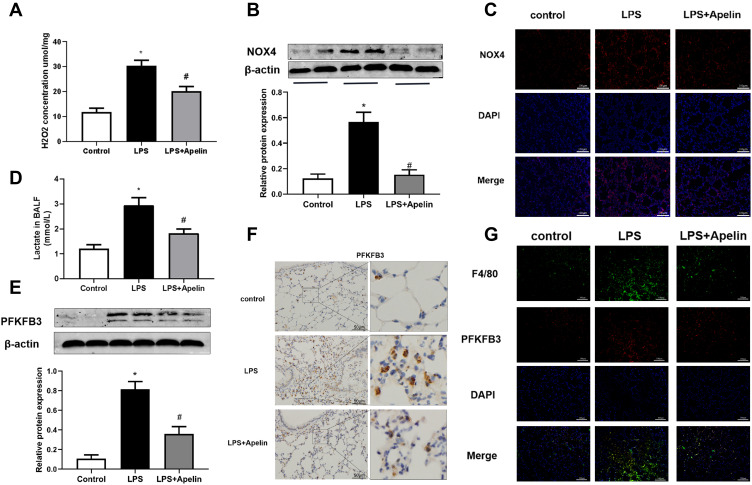
Figure 8.
Apelin-13 alleviated oxidation levels and reduced PFKFB3-driven glycolysis in mice with LPS-induced lung injury. (A) Mice were injected intraperitoneally with apelin-13 or vehicle after LPS instillation, and 6 h later, their lung were harvested. H2O2 concentrations in lung homogenates were tested. (B) NOX4 protein levels in the lungs were detected by Western blot. (C) Immunofluorescence images for NOX4 staining (red) in different groups of lung sections. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Lactate concentrations were detected in different groups of BALF. (E) PFKFB3 protein levels in lung homogenates were assessed by Western blot. (F) The expression of PFKFB3 was detected by immunohistochemistry. (G) Immunofluorescence was performed to examine the colocalization of PFKFB3 (red) and F4/80 (green) in lung sections. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 100 μm. Data were expressed as mean ± SD. *P<0.05 versus control group, #P<0.05 versus the LPS treatment group (n=6).
Abbreviations: LPS, lipopolysaccharide; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; NOX4, NADPH oxidase (NOX) 4; PFKFB3, 6-phosphofructo-2 -kinase/ fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.