Figure 4.
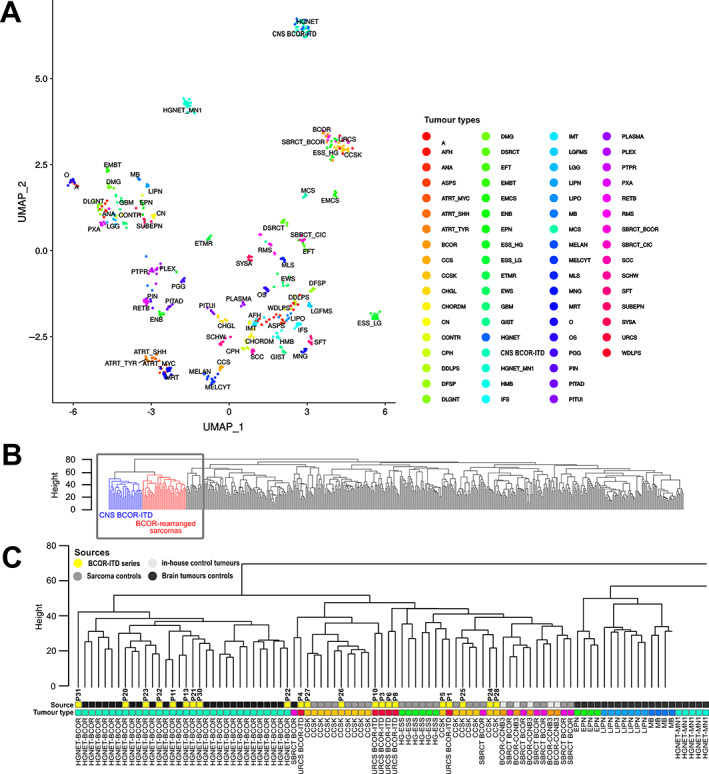
Unsupervised clustering of DNA methylation profiles. (A) UMAP dimension reduction of the 100 first principal components derived from the most variable methylation β values (SD > 0.2, n = 32,500 probes). Twenty‐one BCOR‐ITD samples, with 528 reference tumours (310 brain tumours from Capper et al [29], 212 sarcomas from Koelsche et a. [28], and 6 in‐house BCOR‐CCNB3 tumours). (B) Dendrogram of hierarchical clustering using Euclidian distances and the complete linkage method applied to the same dataset as in (A). Locations of BCOR‐ITD sarcomas and CNS BCOR‐ITD tumours are depicted in red and blue, respectively. The grey square outlines the position of the zoom‐in shown in (C). (C) Zoom‐in on the dendrogram. The ‘Source’ bar refers to the control tumours (light grey for sarcoma cases, dark grey for brain tumours) and the cases of the series in yellow, with the corresponding P numbers. The ‘Tumour type’ bar allocates a tumour type to each case, with the same colour code as in (A) and Figure 3. Abbreviations: A, diffuse astrocytoma IDH mutant; AFH, angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma; ANA, anaplastic pilocytic astrocytoma; ASPS, alveolar soft part sarcoma; ATRT_MYC, atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumour MYC subgroup; ATRT_SHH, atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumour SHH subgroup; ATRT_TYR, atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumour TYR subgroup; CCS, clear cell sarcoma of soft tissue; CCSK, clear cell sarcoma of the kidney; CHGL, chordoid glioma of the third ventricle; CHORDM, chordoma; CN, central neurocytoma; CPH, adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma; DDLPS, dedifferentiated liposarcoma; DFSP, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans; DLGNT, diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumour; DMG, diffuse midline glioma H3K27M; DSRCT, desmoplastic small round cell tumour; EFT, CNS embryonal tumour NOS; EMCS, extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma; EML4‐ALK‐S, EML4‐ALK sarcomas; ENB, esthesioneuroblastoma; EPN, ependymoma; ESS_HG, high‐grade endometrial stromal sarcoma; ESS_LG, low‐grade endometrial stromal sarcoma; ETMR, embryonal tumour with multi‐layered rosettes; EWS, Ewing sarcoma; GBM, glioblastoma; GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumour; HMB, haemangioblastoma; IFS, infantile fibrosarcoma; IMT, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour; LGFMS, low‐grade fibromyxoid sarcoma; LGG, low‐grade astrocytoma and ganglioglioma; LIPN, cerebellar liponeurocytoma; LIPO, lipoma; MB, medulloblastoma; MCS, chondrosarcoma; MELAN, malignant melanoma; MELCYT, melanocytoma; MLS, myxoid liposarcoma; MNG, meningioma; MRT, malignant rhabdoid tumour; O, anaplastic oligodendroglioma; OS, osteosarcoma; PGG, paraganglioma; PIN, pineoblastoma; PITAD, pituitary adenoma; PITUI, spindle cell oncocytoma; PLASMA, plasmacytoma; PLEX, choroid plexus carcinoma; PTPR, papillary tumour of the pineal region; PXA, pleiomorphic xanthoastrocytoma; RETB, retinoblastoma; RMS, rhabdomyosarcoma; SBRCT_BCOR, small blue round cell tumour with BCOR alteration; SBRCT_CIC, small blue round cell tumour with CIC alteration; SCC, squamous cell carcinoma; SCHW, melanocytic schwannoma; SFT, solitary fibrous tumour; SUBEPN, subependymoma; UMAP, Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection
