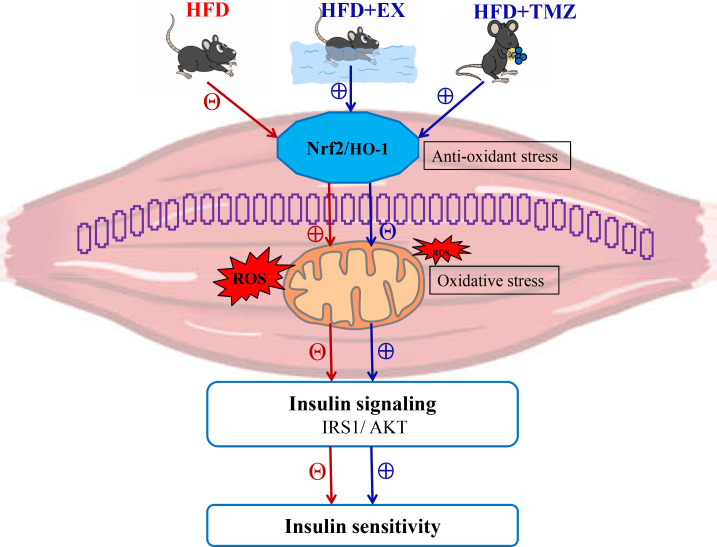
Figure 5.
Proposed pathway of trimetazidine (TMZ) effects on high-fat diet (HFD)-induced muscle insulin resistance (IR). The blue and red arrows show the effects of a HFD and TMZ on physiological processes; ⊕ signals the facilitating effects and Θ the inhibiting effects. Fatty acids stimulate the mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibit the nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway in IR skeletal muscle, contributing to oxidative stress. The excessive ROS production leads to insulin signaling IRS1/AKT (insulin receptor substrate 1/protein kinase B) inhibition and adversely impacts insulin sensitivity. Though, exercise and TMZ were observed to activate Nrf2 signaling control, lowering mitochondrial ROS, resulting in improved insulin sensitivity. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HFD+Ex, HFD+exercise group.