Figure 1.
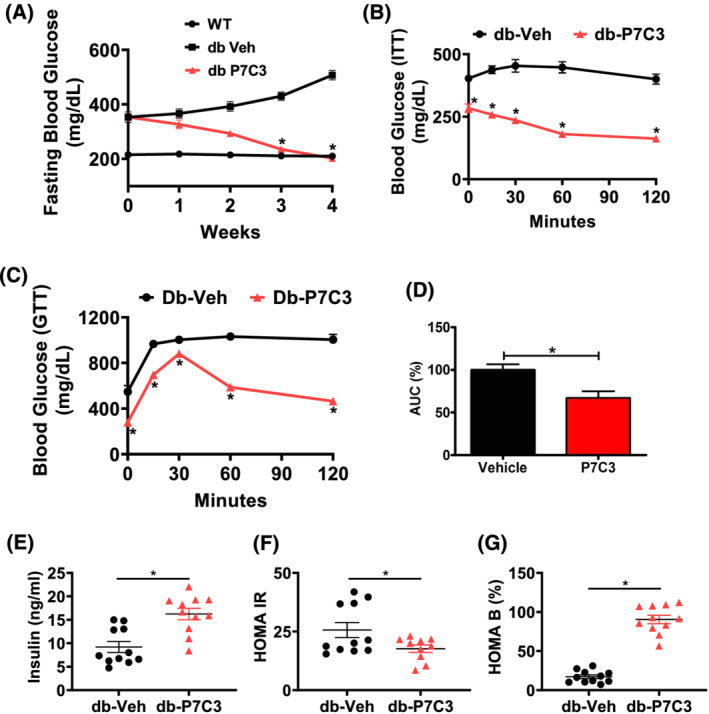
P7C3 reverses hyperinsulinaemia and hyperglycaemia of the diabetic mice. The 16‐week‐old type 2 diabetic (db/db) mice were administered daily with intraperitoneal dose of P7C3 (10 mg/kg/day) or vehicle for 4 weeks. (A) Weekly 6 h fasting blood glucose levels of the db/db mice treated with P7C3 or vehicle (n = 11 each), and the C57Bl/6J WT (n = 6) naïve control mice. (B) Insulin tolerance test (ITT) of 6 h fasted db/db mice injected with 1 U/kg body weight human insulin intraperitoneally (n = 4–5 per group). (C) Glucose tolerance test (GTT) of overnight fasted db/db mice injected with 2 g/kg body weight D‐(+)‐glucose intraperitoneally and measured with GOD‐POD method (n = 5 mice per group). (D) The area under the curve of GTT was obtained using the trapezium method and expressed in percentage. (E) The circulating insulin levels in blood serum and (F) homeostatic model of insulin resistance (HOMA IR) and (G) homoeostatic model of pancreatic β‐cells (HOMA B) expressed in percentage. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05; P7C3 vs. vehicle‐treated db/db mice. The age‐matched WT mice were used as naïve control to determine the baseline weekly fasting blood glucose levels.
