FIGURE 4.
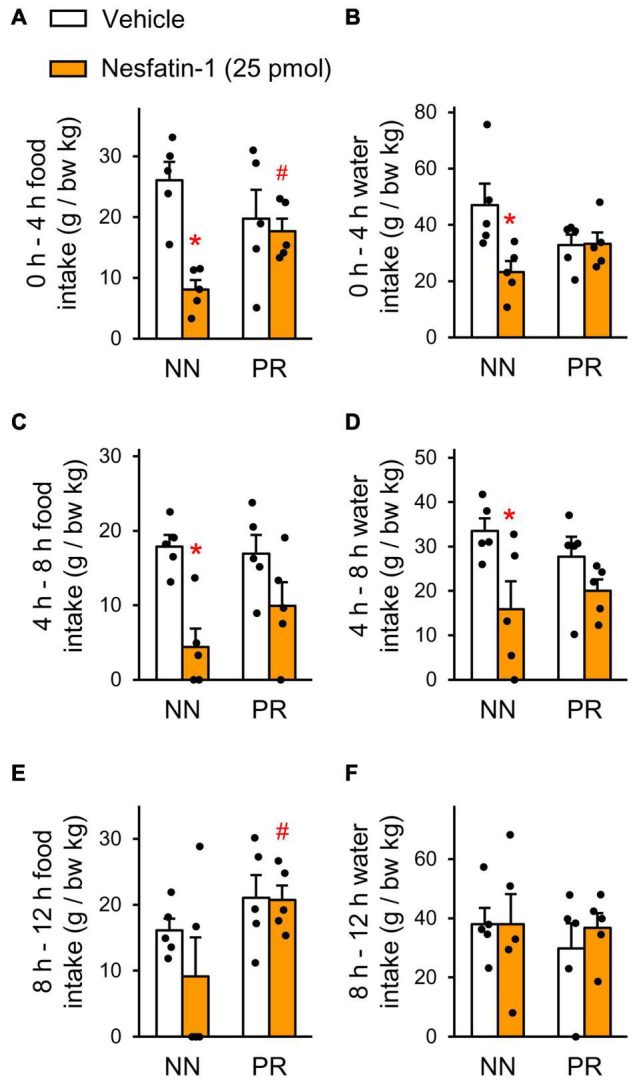
Effect of acute intracerebroventricular (icv) injection of nesfatin-1 (25 pmol), or vehicle on nocturnal food and water intakes of NN and PR rats. Food (A,C,E) and water (B,D,F) intakes of 12 week-old NN and PR rats were measured at 4 h intervals. Zero is the timepoint of treatments. (A,B) 0–4 h. Two-way ANOVA, food intake, effect of treatment F(1, 16) = 10.43, p = 0.005 treatment × phenotype: F(1, 16) = 6.530, p = 0.021, water intake, treatment × phenotype: F(1, 16) = 5.66, p = 0.030. (C,D) 4–8 h. Two-way ANOVA food intake, effect of treatment: F(1, 16) = 16.85, p < 0.001, water intake, effect of treatment: F(1, 16) = 8.51, p < 0.010. (E,F) 8–12 h. Two-way ANOVA, effect of phenotype: F(1, 16) = 5.04, p = 0.039; NN vs. PR within nesfatin-1, p = 0.041. Effects of nesfatin-1 are impaired in PR rats. Tukey multiple comparison tests, *p < 0.05 vs. NN-vehicle, #p < 0.05 vs. NN-nesfatin-1. Means ± SEM, n = 5 for all graphs.
