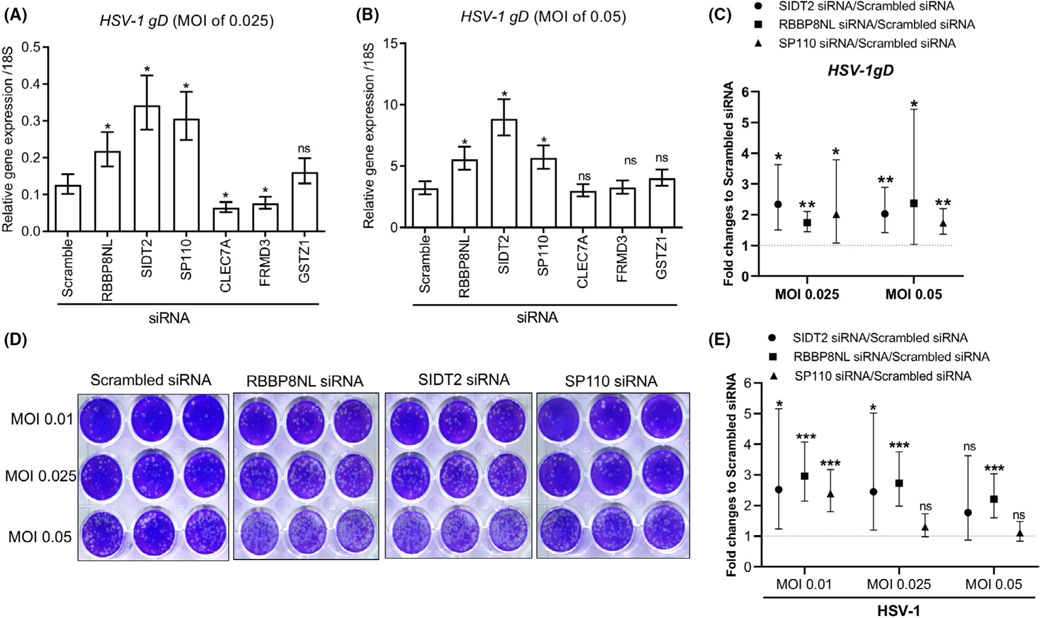
FIGURE 1.
Silencing SIDT2 and RBBP8NL led to enhanced HSV-1 replication in NHPK. NHPK were transfected with scrambled and candidate gene siRNA duplexes for 48 hours. The cells were then infected with HSV-1 with indicated MOI for 24 hours. HSV-1 gD expression was evaluated with qRT-PCR in samples treated with different MOI of HSV-1 at 0.025 (A) and 0.05 (B). (C) HSV-1gD expression was evaluated by qRT-PCR in NHPK treated with scrambled SIDT2, RBBP8NL, and SP110 siRNA. Results of three (SP110) or four (SIDT2, RBBP8NL) independent experiments were combined. For panels A, B and C, data are presented as the geometric mean (95% CI) of the fold change between target siRNA and scrambled siRNA. In panels A and B, comparisons of log-transformed relative gene expression were made using Dunnett's test with Scrambled siRNA as the control. In panel C, comparisons of log-transformed relative gene expression were made using t tests. Significant differences had *p-value < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; ns = not significant. (D) Representative pictures of HSV-1 viral plaque assays. (E) The quantitative results of viral plaque-forming units from five independent experiments