Fig. 5.
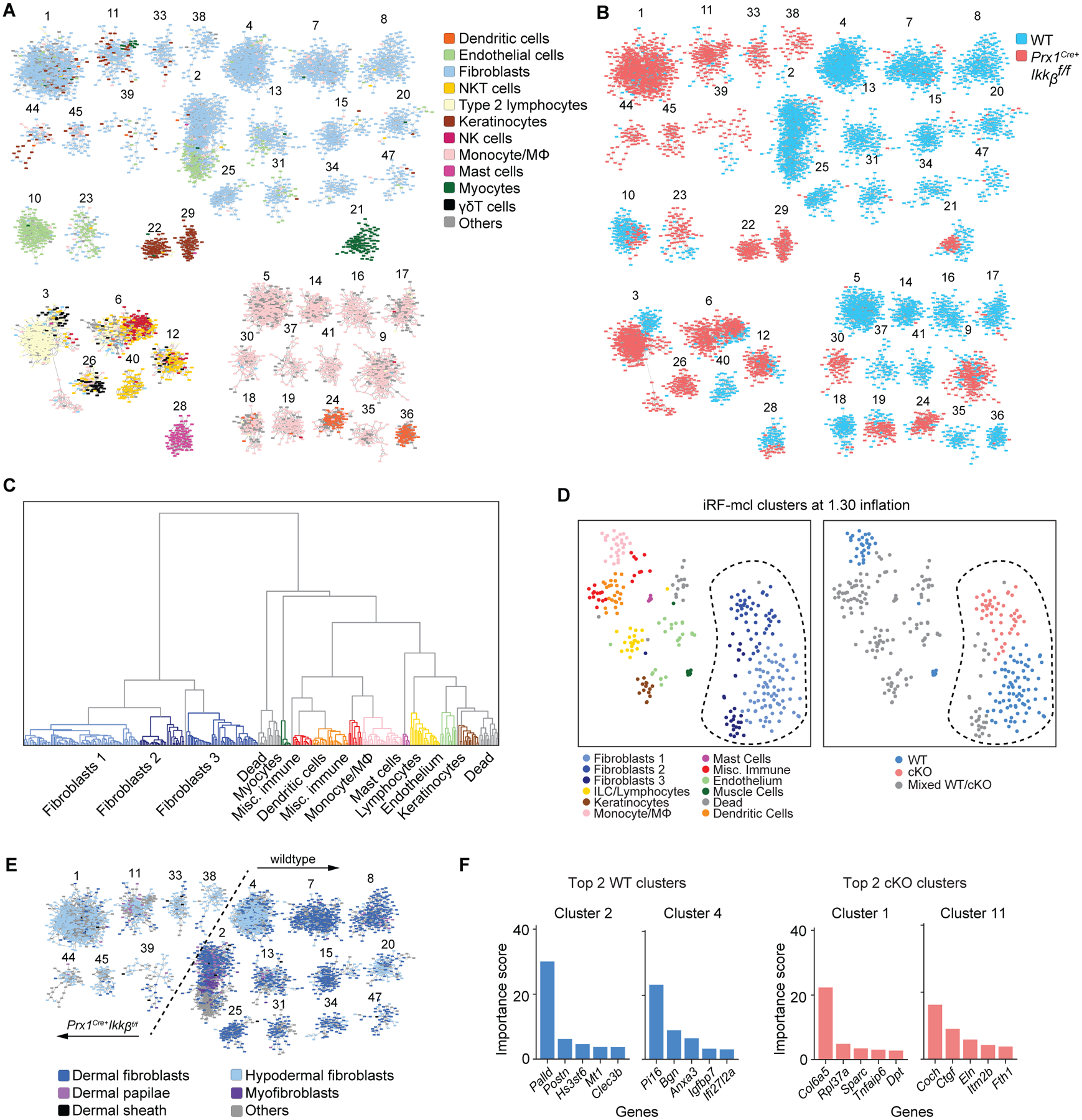
Single cell RNA sequencing reveals marked changes in fibroblast transcriptome by the Ikkb gene deletion. A. iRF-MCL (iterative random forest-Markov clustering) of 11084 cells from enzymatically digested ventral skin of WT and Prx1Cre+Ikkbf/f mice with cell type designation based on putative gene expression. Clusters with >50 cells are shown. B. WT (blue) and cKO (Prx1Cre+Ikkbf/f, red) group designation demonstrating even distribution of sample (3566 cells from WT, 2510 cells from cKO are shown). C. Hierarchical partitioning of Markov clusters and cell type designation, using Ward’s linkage method between Pearson correlations of mean expression vectors of the clusters. The groups generated by this partitioning have been t-SNE projected in Figure 5D and share the same color legend. D. t-SNE plot with cell type designation (left) and WT/cKO designation (right) demonstrating clear separation of fibroblast clusters (encircled in dashed line) derived from Ikkb-deleted group. Mixed WT/cKO cluster threshold was determined at <0.90 cutoff. E. Fibroblast subtyping based on (36) demonstrating a transcriptomic shift towards that of hypodermal fibroblasts when Ikkb is deleted (left of the dashed line). F. Importance score for genes that determined the formation of top 2 clusters from WT and cKO groups as characterized in A and B.
