Fig. 3. Brain system segregation declines most in older adults without a college degree.
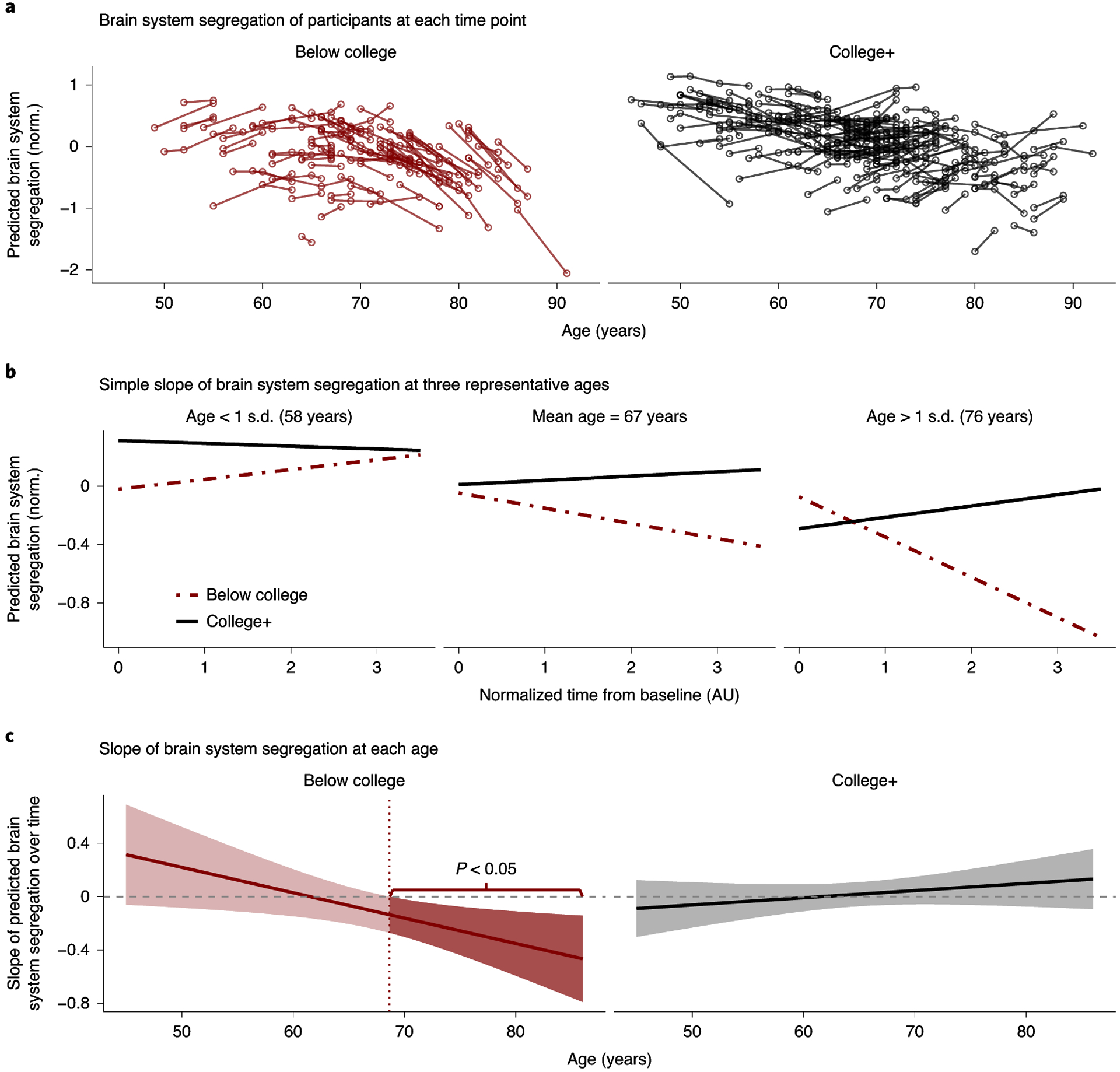
a, Predicted brain system-segregation values from the linear mixed-effects model plotted against a participant’s age when the brain scan was acquired. A greater decline in brain system segregation is evident in participants who are older (~65 years and over) and without a college degree than in more educated individuals. Norm., normalized. b, Simple slope analysis depicts the predicted slope of brain system segregation at three representative ages: 58, 67 and 76 years (age < 1 s.d., mean age and age > 1 s.d. across the entire sample, respectively). Brain system segregation declines in older participants without a college degree (dashed red line, middle and right (ages 67 and 76 years) but stays relatively flat for individuals with a college degree regardless of age (solid black lines). AU, arbitrary units. c, A Johnson–Neyman analysis fully illustrates how changes in brain system segregation over time (y axis) differ based on the participant’s age (x axis) and educational attainment. The predicted slope calculated from the linear mixed-effects model for each age within both education groups is illustrated; envelopes represent CI95%. In participants without a college degree (left), the analysis identifies the ages at which longitudinal changes in brain system segregation are statistically significant (darker shade represents a slope with P < 0.05, where the CI95% of the slope does not cross 0). The decline in brain system segregation is statistically significant for individuals without a college education starting at approximately 69 years of age; reliable changes in brain system segregation are not evident at any segment of age for those with a college degree (right). To facilitate the comparison between both education groups, the slopes of predicted brain system segregation for both ‘below college’ and ‘college+’ groups are shown for the full age range of the entire sample (45–86 years).
