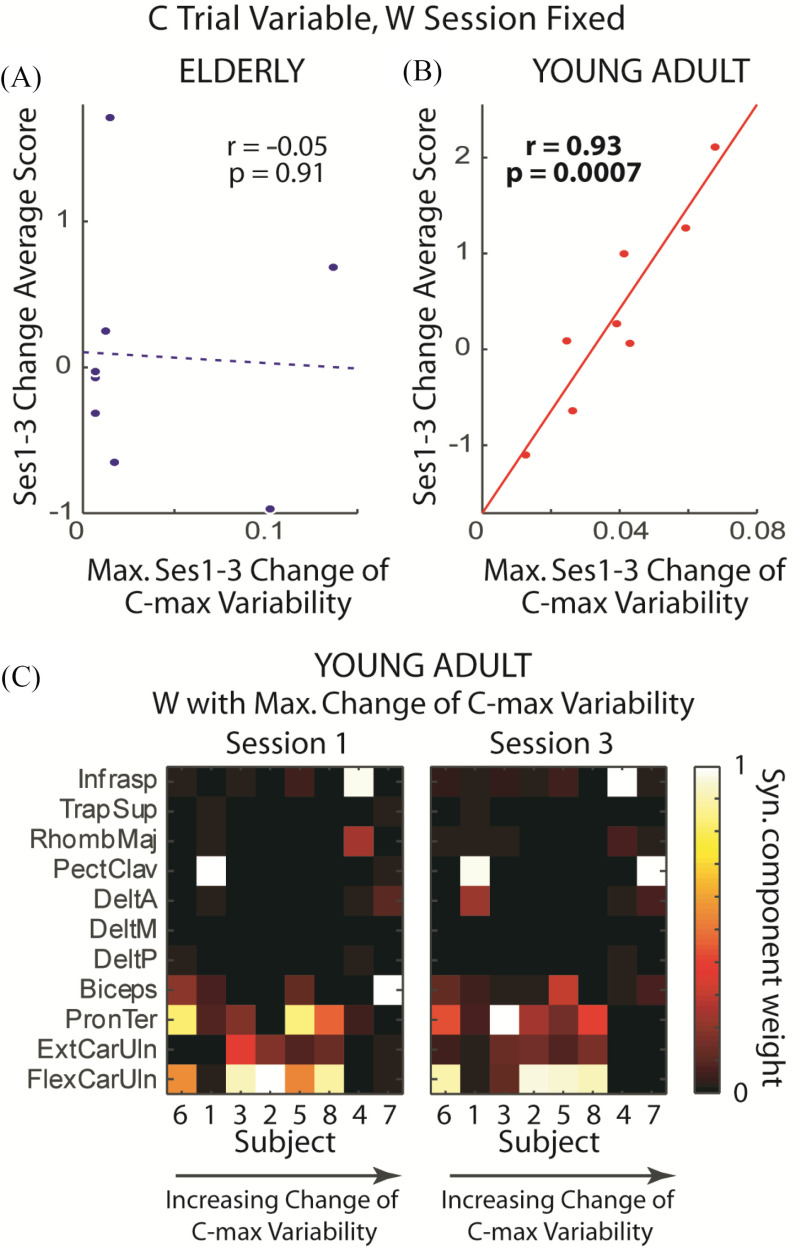
Figure 3.
Characterization of C-magnitude variability when W was fixed across the trials of a session. A,B, In both age groups, the change of average bowling score was correlated against the maximum (across each subject's synergies) session-1-to-3 change of Cmax variability. A highly statistically significant correlation was found in young adults (B, solid line) but not elderlies (A, dotted line). r, Pearson's correlation coefficient; p, the p-value of the correlation. C, The muscle synergies (W) showing maximum Cmax variability in the young adults (each row corresponds to a muscle; each column, a subject). Note consistency of these session-fixed W's from session 1 to 3. Also note how muscles including Biceps, PronTer, and FlexCarUln were consistently recruited. Interestingly, their biomechanical functions – wrist/elbow flexion and wrist internal rotation – align with those demanded of high-scoring bowlers [39].