Figure 4.
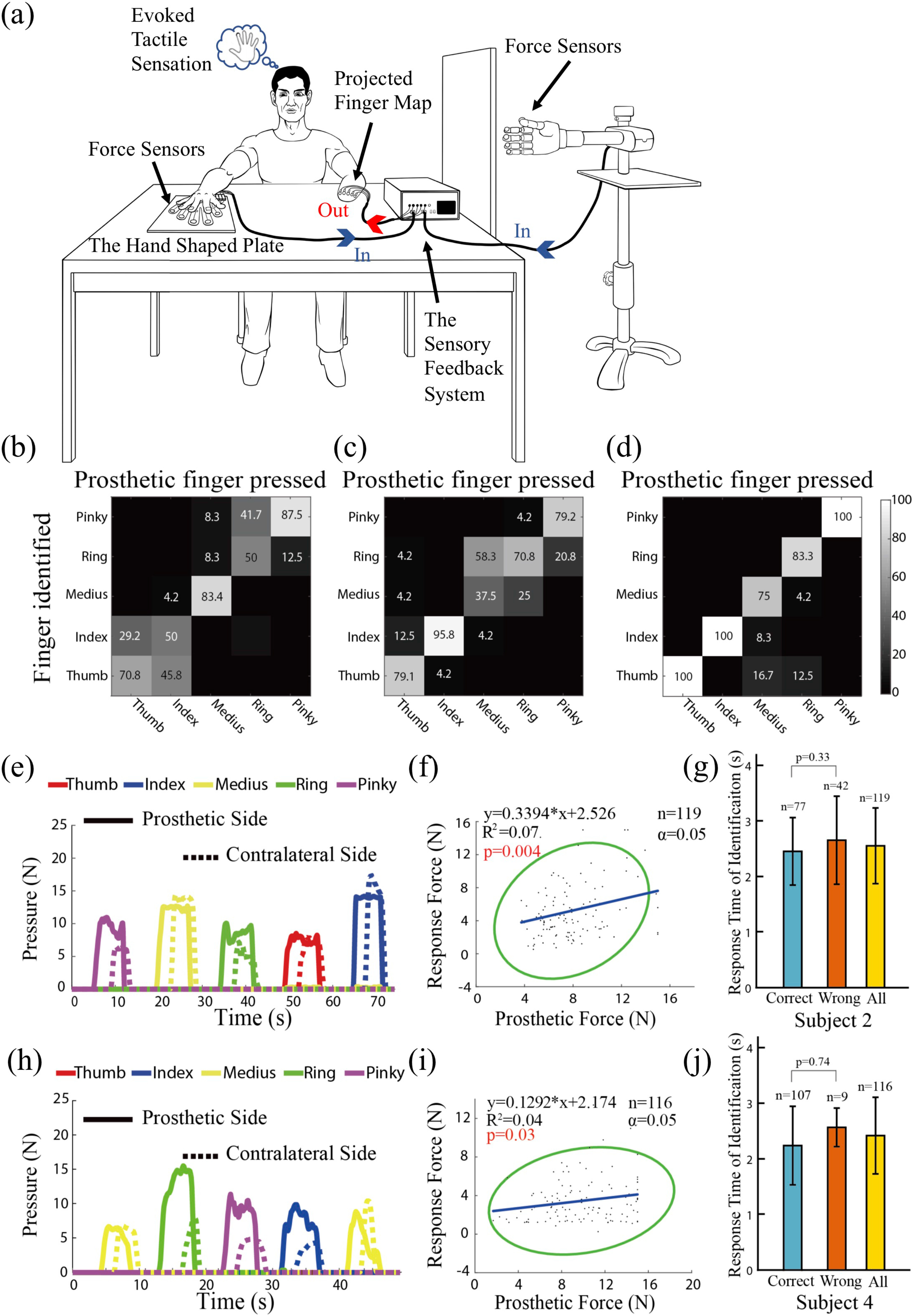
Results of the finger-to-finger identification experiment by Subject 2, Subject 3 and Subject 4. (a) Experimental setup, in which the subject sensed the pressure of a prosthetic finger by way of a multi-channel sensory feedback system, then pressed the sensors on a hand shaped plate using contralateral fingers. The experiment is demonstrated in Video 1 and Video 2. Confusion matrixes (b) - (d) present the accuracy of finger-to-finger identification of the three subjects. (e) and (h) depict response force of contralateral fingers by Subject 2 and Subject 4, respectively. The correlation between the response force and the prosthetic pressure force is illustrated in (f) and (i). The corresponding 95% confidence ellipses surrounded all paired force points whether the identification was correct or wrong. (g) and (j) show the response times with correct, or wrong identification, and all identifications.
