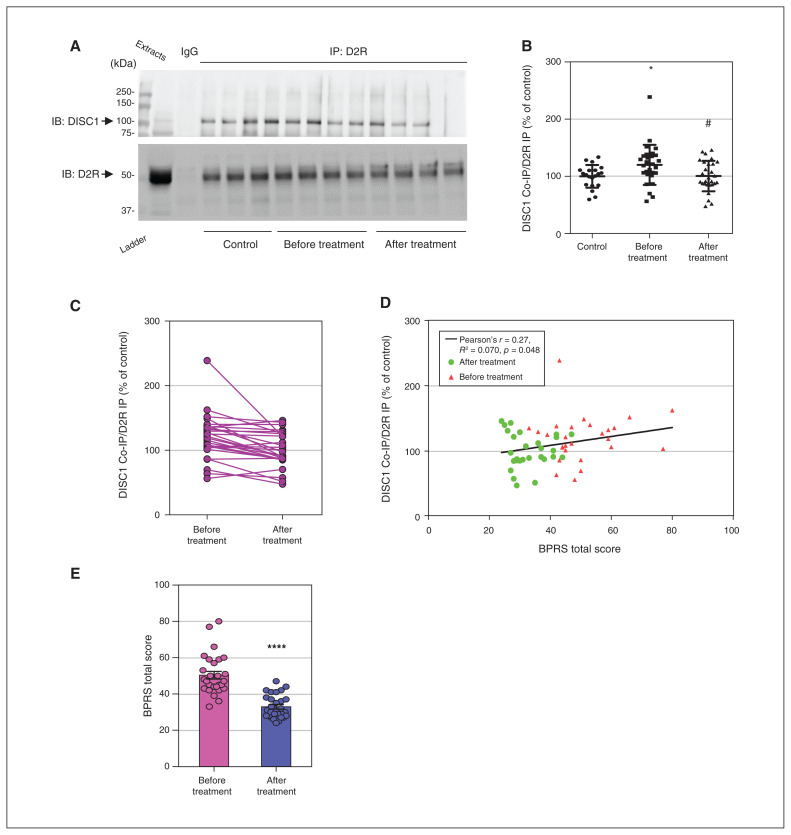
Figure 2.
Antipsychotic medications normalized elevated D2R-DISC1 complex levels in peripheral blood samples from patients with schizophrenia (Shanghai second cohort). (A) Coimmunoprecipitation shows that antipsychotic medications reduced D2R-DISC1 complex levels in peripheral blood samples from patients with schizophrenia. (B) Densitometric analysis of DISC1 coimmunoprecipitated by D2R from peripheral blood samples of patients with schizophrenia before and after antipsychotic treatment, and of unaffected controls. *p < 0.05 versus controls, #p < 0.05 versus patients with schizophrenia before treatment. One-way analysis of variance followed by a Tukey post hoc test (n = 28 patients with schizophrenia before and after treatment; n = 20 unaffected controls). (C) Graph displaying D2R-DISC1 complex levels before and after treatment. (D) BPRS total score was positively correlated with D2R-DISC1 complex levels in patients with schizophrenia before and after anti-psychotic treatment (n = 28 participants with schizophrenia). (E) BPRS total scores for patients with schizophrenia before and after treatment; t test, ****p < 0.001 compared to before treatment. BPRS = Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; Co-IP = coimmunoprecipitation; D2R = dopamine 2 receptor; DISC1 = disrupted in schizophrenia 1; IB = immunoblotting; IgG = immunoglobulin G; IP = immunoprecipitation.