Fig. 1.
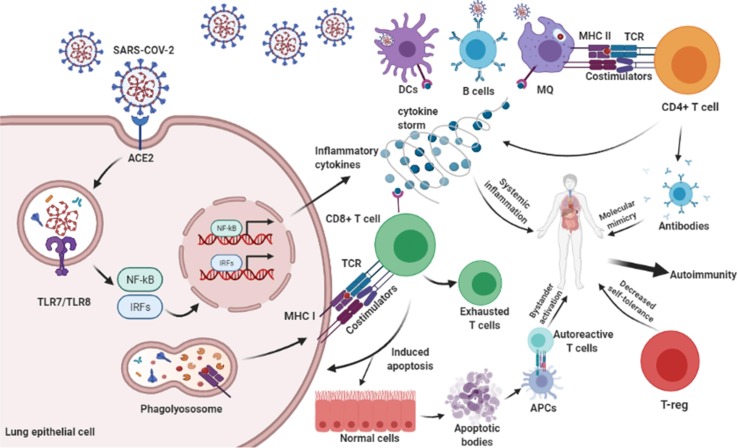
The SARS-CoV-2 proliferates by binding to ACE-2 receptor on the surface of host epithelial cell. Intracellular signaling pathways are activated and produce inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IFN-β, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-17, and IL-18 that may cause autoimmunity via systemic inflammation. APCs process the antigens and present them to TCD4+ cells. Activated TCD4+ cells have a role in inflammatory cytokine secretion, MQ activation, and antibody formation. Antibody against the viral antigen can recognize host tissue antigens that cause autoimmunity. Also, TCD8+ cells can detect viral antigens via TCR-MHC I and cause apoptosis in virus-infected and uninfected cells mainly via perforin-granzyme and Fas and its ligand. This procedure is named bystander activation and causes autoimmunity. The apoptotic bodies which contain self-antigens are presented to autoreactive T cells and cause autoimmunity. Given that autoimmunity is driven by recognition of self-antigen and CD8 T-cell exhaustion dependent on chronic antigen stimulation, T-cell exhaustion could facilitate the retention of antigen-specific T cells in the repertoire under chronic stimulation. Also, the reduction of T-reg by the SARS-CoV-2 reduces self-tolerance and leads to autoimmunity.