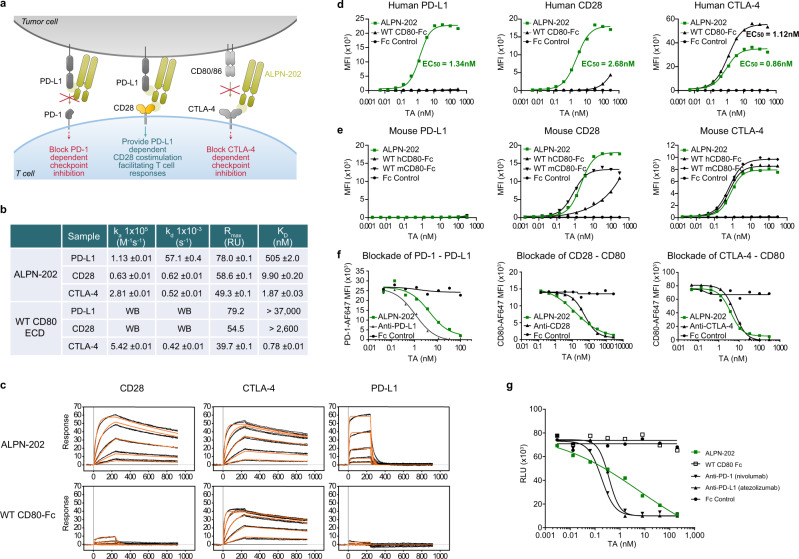
Fig. 1. ALPN-202, a variant CD80 IgV domain Fc fusion, binds human PD-L1, CD28, and CTLA-4 with high affinity.
a Schematic illustrating the three mechanisms of action of ALPN-202: blockade of PD-1–PD-L1 interaction, PD-L1-dependent CD28 costimulation, and blockade of CTLA-4–CD80/CD86 interactions. b, c Affinity measurements of ALPN-202 and WT CD80-Fc to monomeric wild type PD-L1, CD28, and CTLA-4 were determined by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Sensorgrams are shown in black lines and results from non-linear least squares regression analysis of the data in orange lines. Sensorgrams were global fit to a 1:1 binding model for triplicate injections of human CD28, CTLA-4, and PD-L1 against captured ALPN-202 and WT CD80-Fc surfaces. For the weak CD28–WT CD80-Fc and PD- L1–WT CD80-Fc interactions, the theoretical Rmax was used as a fixed parameter in the global fit to estimate the KD. WB, weak binding; WT, wild type; ECD, extracellular domain. d, e ALPN-202 binding to CHO cells stably expressing human or mouse PD-L1, CD28, or CTLA-4. ALPN-202 displayed higher affinity for human PD-L1 and CD28, and comparable affinity for CTLA-4, relative to WT CD80-Fc. ALPN-202 did not bind to mouse PD-L1 but did bind mouse CD28 and CTLA-4 with comparable affinity as WT mouse CD80-Fc. TA test article; MFI median fluorescent intensity. f ALPN-202 blocked binding of PD-1-AF647 to cell surface PD-L1 and CD80-AF647 to cell surface CD28 and CTLA-4 to CD80 measured by flow cytometry. g ALPN-202 blocked human PD-L1-mediated recruitment of SHP-2 to PD-1 in a cell-based assay. RLU, relative luminescence units. Experiments in (d–g) were conducted two times and data shown are representative. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.