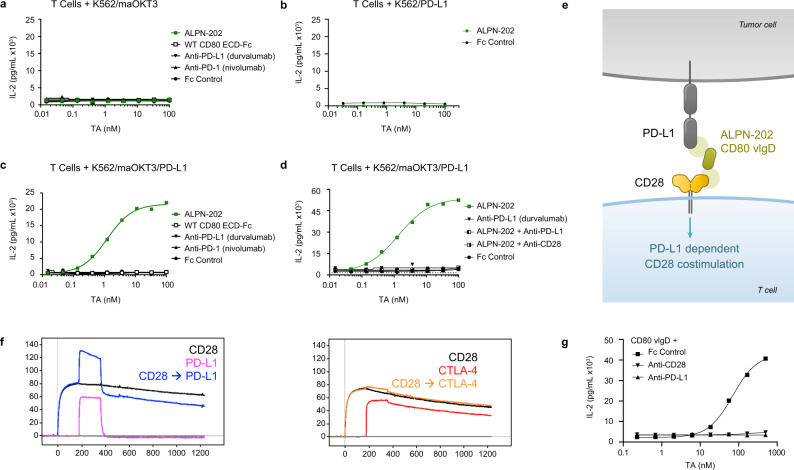
Fig. 2. CD28 costimulation by ALPN-202 requires TCR activation and co-binding to PD-L1.
Primary human T cells, were co-cultured for 24 h with test articles (TA) and K562 cell artificial antigen-presenting cells (aAPC) expressing membrane anchored anti-CD3 clone OKT3 (maOKT3), PD-L1, or both. a In the absence of PD-L1 to anchor ALPN-202 on the aAPC, no increase in IL-2 was detected above background. b In the absence of TCR stimulation (via maOKT3), no increase in IL-2 was observed. c When both maOKT3 and PD-L1 were present on the aAPC, ALPN-202 (green line) induced a strong dose-dependent costimulatory signal above that of WT CD80 ECD-Fc or PD-(L)1 blockade alone. WT wild type; ECD extracellular domain. d The costimulatory activity of ALPN-202 was inhibited when combined with blocking antibodies to either PD-L1 or CD28, confirming the requirement for dual binding to induce costimulation. e Schematic illustrating how a monomeric (no Fc) CD80 variant Ig domain (vIgD) binds PD-L1 and engages CD28 in trans. f Overlaid SPR sensorgrams for two paired serial injections of monomeric CD28 (black line) followed by PD-L1 (blue line) or CTLA-4 (orange line) against ALPN-202 surfaces. Data were collected using two serial 180 s, 1500 nM injections. Single analyte injections of PD-L1 (pink line) or CTLA-4 (red line) were made by pairing with blank buffer injections. g Primary T cells were co-cultured with K562/maOKT3/PD-L1 cells and a titration of the monomeric ALPN-202 CD80 vIgD with saturating anti-PD-L1 antibody, anti-CD28 antibody, or Fc control for 24 h. For (a–d), and (f), each data point is mean concentration of IL-2 for each sample run in duplicate wells. Data shown are representative of three separate donors run independently. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.