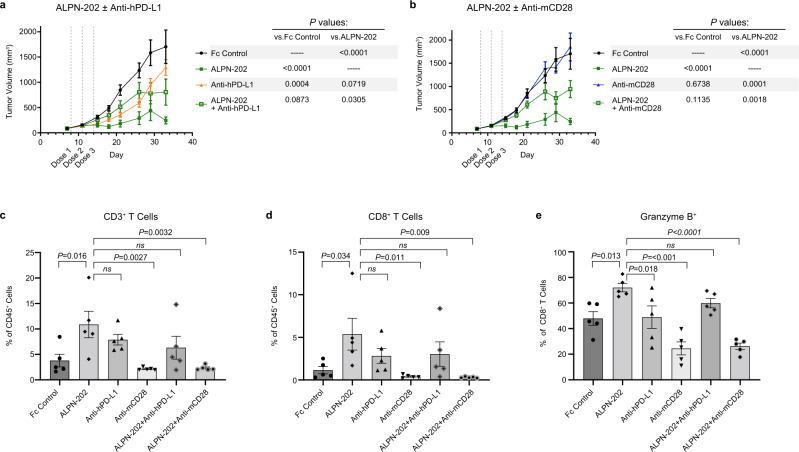
Fig. 6. ALPN-202 increases intratumoral inflammatory cell infiltrate in part by hPD-L1-dependent mCD28 costimulation.
a, b The anti-tumor activity of ALPN-202 was significantly blocked by combining with (a) anti-hPD-L1 or (b) anti-mCD28 blocking antibodies (n = 12 mice/group). Mean tumor volumes ± SEM are shown. Tumors were collected from mice 48 h after the second dose, dissociated, and analyzed by flow cytometry. ALPN-202 treatment significantly increased the percentage of infiltrating total CD3+ T cells (c), CD8+ T cells (d), and granzyme B+ CD8+ T cells (e) relative to Fc Control treated animals. In each case, this influx in T cells was reduced when ALPN-202 was combined with anti-hPD-L1 or anti-mCD28 antibodies. Statistical significance was determined by repeated-measures two-way ANOVA for treatment effects (a, b) or one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (c–e). Bar height indicates mean value ± SEM and symbols represent individual tumor samples (n = 5 tumors per treatment group) (c–e). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.