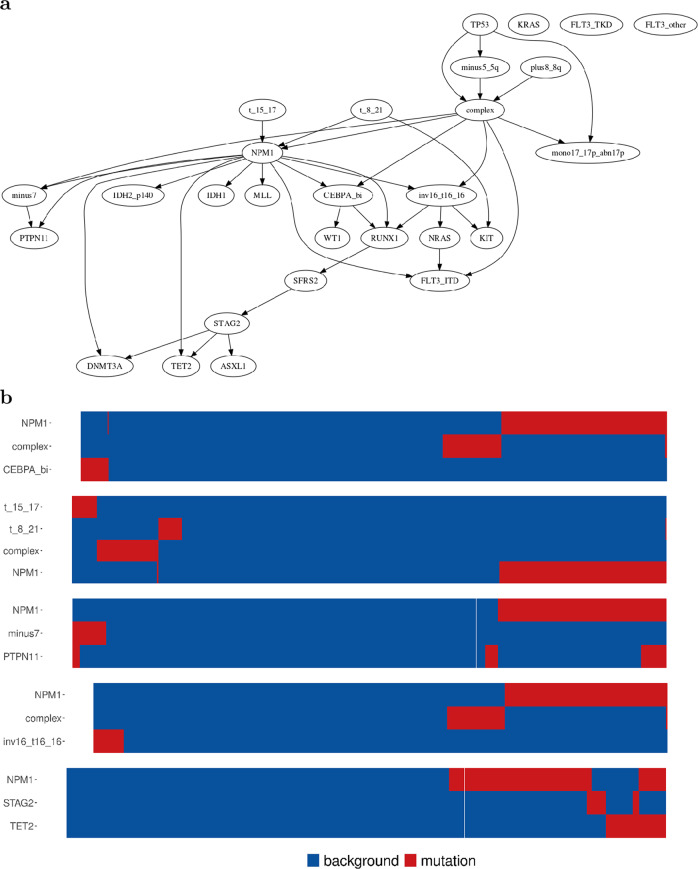
Fig. 2. Bayesian network learnt for AML patient data.
a AML Bayesian network learned with Gobnilp (μ = 60, ϵ = 7). This is the vanilla output of the learning algorithm. b Family heatmaps. The complex probabilistic relationships within a Bayesian network can be broken to a number of more easily understood units. We form such units, also called families in BNs, from each node and all nodes from which an arrow points to this single node. We use heatmaps to easily communicate these relationships. Here a number of family heatmaps from the AML Bayesian network (μ = 60, ϵ = 7) are shown. For example, the first heatmap shows family NPM1-complex-CEBPA_bi. Blue plots lack of driver event while red shows presence of the event. Patients are plotted on the x-axis. Thus the red cluster on the bottom left of the top heatmap plots a number of patients that have the CEBPA_bi event but do not have the complex event.