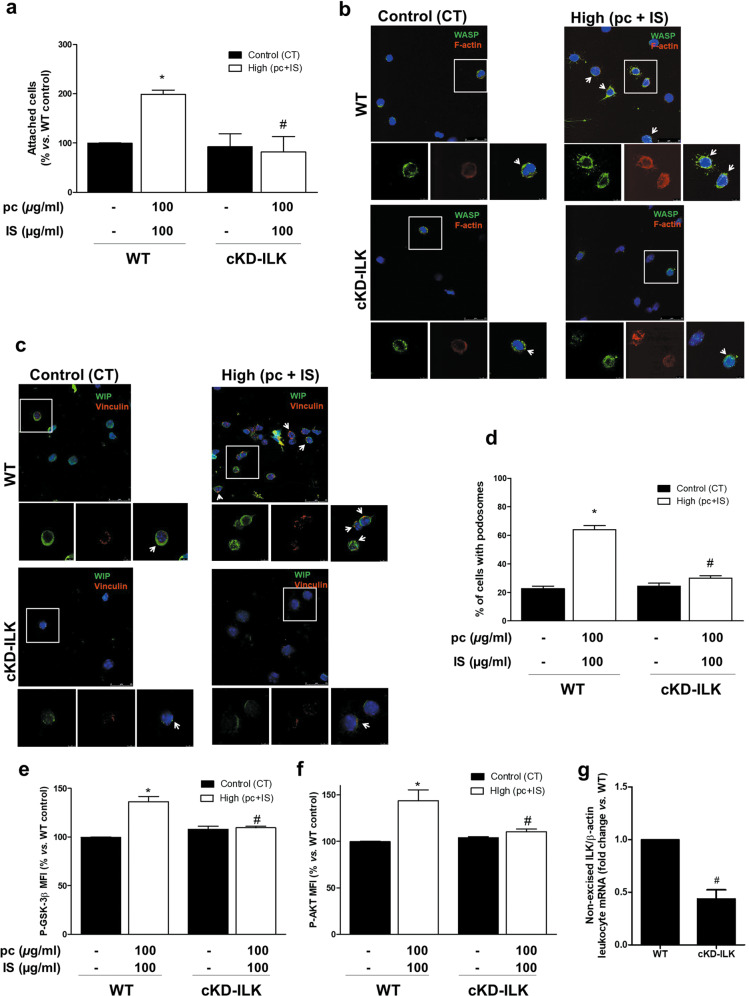
Fig. 8. ILK depletion prevents ex vivo increases in podosome formation and adhesion to a fibronectin matrix in mouse leukocytes and the molecular mechanism downstream of ILK activation induced by p-cresol (pc) plus indoxyl sulfate (IS) treatment.
CRE-LOX mice were injected with tamoxifen (ILK conditional-knockdown [cKD-ILK] mice) or vehicle (wild-type [WT] mice) to induce ILK deletion. Leukocytes were obtained, seeded on fibronectin-coated coverslips, and incubated with high concentrations of pc plus IS for 24 h. a Bar graphs indicating the average percentage of leukocytes attached to the fibronectin matrix as determined by fluorescence confocal microscopy. b, c The podosome formation of leukocytes stained with phalloidin (red) and a WASP antibody (green) (b) or vinculin (red) and WIP (green) antibodies (c) as well as Hoechst 33342 (blue) was determined by fluorescence confocal microscopy. The results of a representative experiment are shown. Magnifications of the boxed area are shown at the bottom. Scale bars: 25 and 5 μm. d Bar graphs indicating the mean percentage of cells with podosomes per field of view for cells treated as described above. e, f Median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of GSK-3β pS9 (e) and AKT pS473 (f) in the leukocyte cell population as analyzed by flow cytometry. The results are expressed as a percentage of the WT control (untreated). g Uncleaved ILK mRNA expression in leukocytes was quantified by RT–qPCR. The relative fold changes in mRNA content vs. those in the WT group after normalization to total β-actin content (the endogenous control) are presented. The values are presented as the mean ± SEM from 3 or 5 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. WT control; #P < 0.05 vs. (pc + IS) WT.