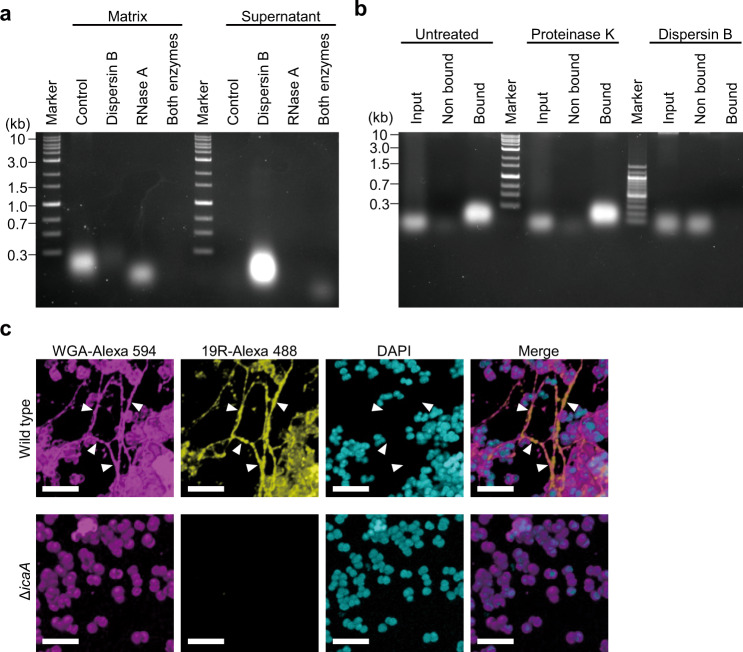
Fig. 5. Polysaccharides capture external RNA in the biofilm.
a A biofilm matrix was extracted from MR10 24-h biofilms formed in BHIN. Dispersin B alone, RNase A alone, or both enzymes were added to the biofilm immediately before the biofilm-matrix extraction. After incubation for 1 h at 37 °C, the treated samples were centrifuged. After centrifugation, the supernatants were collected and the biofilm matrices were extracted from the pellets using 1.5 M NaCl. The nucleic acids were analyzed using agarose gel electrophoresis. b RNA pull-down was performed as illustrated in Supplementary Fig. 4. Biofilm-associated and nonassociated RNA from MR10 wild type pretreated with proteinase K and dispersin B or left untreated were detected using agarose gel electrophoresis. c The biofilms of MR10 wild-type and its isogenic ΔicaA strains were cultured in BHINC supplemented with 19R-Alexa 488 for 24 h at 37 °C. The biofilms were stained with WGA-Alexa 594 and DAPI. Subsequently, the biofilms were observed by high-resolution CLSM (with Airyscan unit). WGA-Alexa 594 and DAPI stained the polysaccharides and the cell wall (magenta) and DNA (cyan), respectively. 19R-Alexa 488 indicates localization of RNA (yellow). The merged images are also shown. Scale bars correspond to 5 µm. The arrowheads indicate colocalization of polysaccharides and RNA.