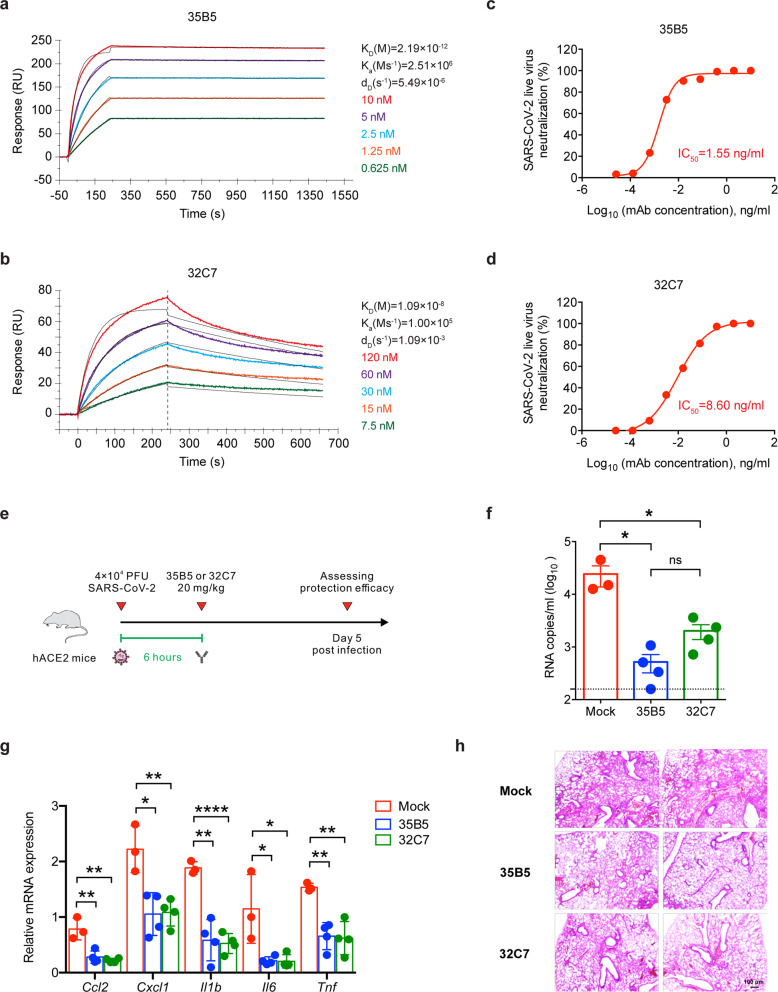
Fig. 1.
35B5 and 32C7 protect against authentic SARS-CoV-2 virus. a, b Affinity analysis of 35B5 (a) and 32C7 (b) binding to immobilized SARS-CoV-2 RBD by using SPR. The experimental data were calculated using a 1:1 binding model. c, d In vitro neutralizing activity of 35B5 (c) and 32C7 (d) against authentic SARS-CoV-2. The mixture of SARS-CoV-2 and serially diluted 35B5 or 32C7 were added to Vero E6 cells. After 48 h, IC50 values were calculated by fitting the viral RNA copies from serially diluted mAb to a sigmoidal dose–response curve. e Schematic diagram of 35B5 and 32C7 treatment in vivo. Six hours after infection with 4 × 104 PFU SARS-CoV-2, the hACE2 mice received a single dose of 35B5 or 32C7 with 20 mg/kg or no mAb treatment (mock). At day 5 post infection, lung tissues were collected for viral burden assessment, cytokine/chemokine assay and histological analysis. f Viral titers in the lungs were measured by qRT-PCR and presented as RNA copies per milliliter of lung abrasive fluid. g Gene expressions of cytokines and chemokines in the lungs were determined by qPT-PCR. h Histopathological analysis of lung tissues. The data are representative of at least two independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001. ns not significant. Error bars in (f) and (g) indicate SD