Figure-2.
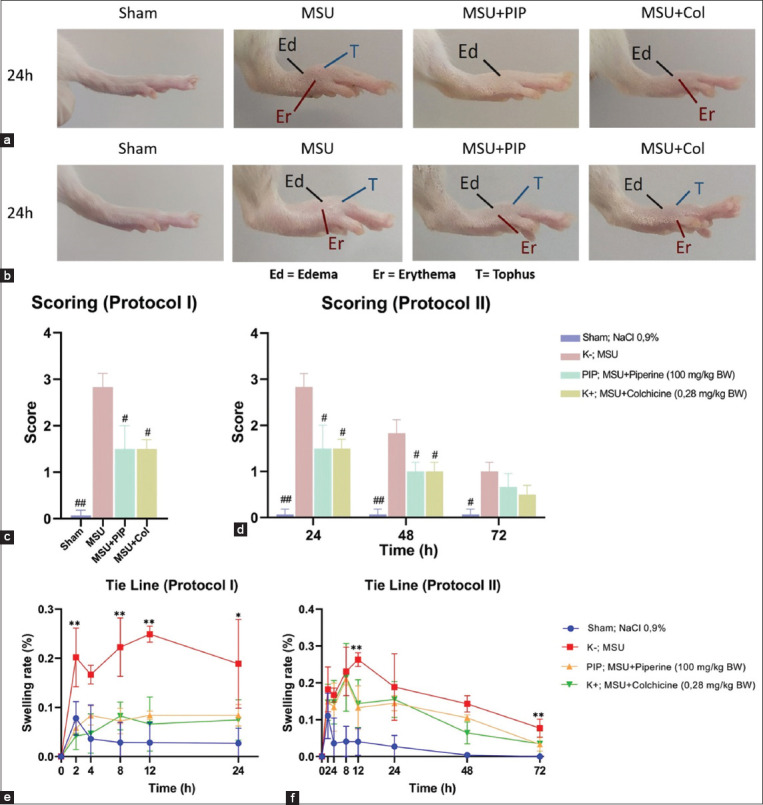
Oral administration of PIP suppresses gouty inflammation induced by injection of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in rat plantar. (a, c, e) Anatomical assessment of inflammation in preventive protocol I. (b, d, f) Anatomical assessment of inflammation in curative protocol II (a) comparison of rat paw morphology of protocol I 24 h post-injection. (b) Comparison of rat paw morphology of protocol II 24 h post-injection. (c) Protocol I rat plantar inflammation scoring 24 h post-injection. (d) Protocol II rat plantar inflammation scoring 24, 48, and 72 h post-injection. (e) The swelling rate of protocol I rat paws was calculated using the tie line method at 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 h post-injection. (f) The swelling rate of protocol II rat paws was calculated using the tie line method at 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h post-injection. Values on the graph are represented as mean±SD (n=3 rats/group). Significantly different from MSU group, #p<0.05, ##p<0.01; significantly different from sham, MSU+PIP, MSU+Col groups, *p<0.05, **p<0.01. MSU=Monosodium urate; PIP=Piperine; Col=Colchicine.
