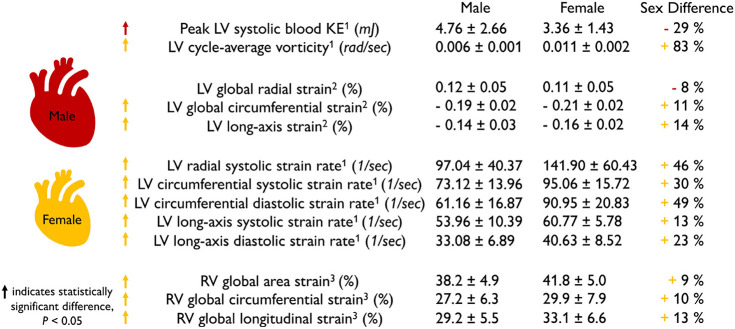
Table 2.
Sex differences in healthy myocardial strains.
Sex differences between female and male flow, strain, and strain rate, with a male as the baseline. While the male heart has greater systolic blood kinetic energy, the female heart exhibits strains that are significantly larger than the male for radial, circumferential, and longitudinal axes and both left and right ventricular chambers of the heart. Negative values in red indicate that the female parameter is smaller, positive values in yellow indicate that the female parameter is larger; arrows indicate reported statistically significant differences; quantitative data are represented as mean absolute value ± SD; [1] Rutkowski et al. (2020); [2] Lawton et al. (2011); [3] Lakatos et al. (2020).