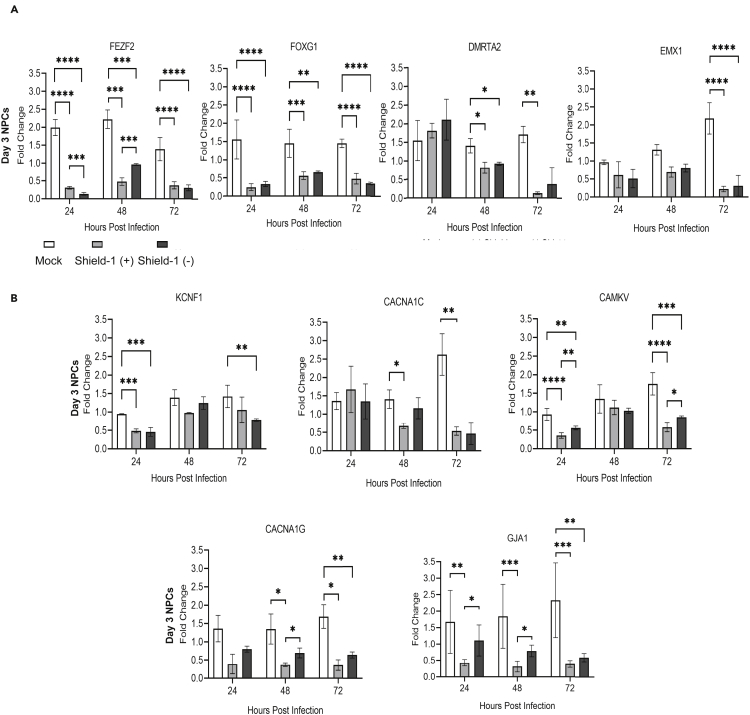
Figure 7.
Cellular gene targets are downregulated within NPCs infected with TB40r mGFP-IE-FKBP with varying dependence on Shield-1 administration
qPCRs were performed for several key neurodevelopmental transcription factors (FezF2, FOXG1, DMRTA2, and EMX1) and signaling, cell-cell communication, and junctional genes (CACNA1C, CACNA1G, CAMKV, KCNF1, and GJA1) within the HCMV-IE1/IE2-ddFKBP-infected (Shield +) and (Shield –) groups plus uninfected (Mock) NPCs at 3 days post plate down.
(A) No robust or consistent effect of Shield administration was observed for these targets; instead, genes were downregulated regardless of administration at all time points.
(B) Downregulation of KCNF1, CACNA1C, CAMKV, CACNA1G, and GJA1was observed regardless of Shield administration; however, trends toward an effect of Shield-1 administration can be observed for CACNA1C at 48 hpi or CAMKV at 72 hpi. A significant Shield-1-dependent effect was noted for genes CACNA1G and GJA1 at both 48 and 72 hpi. Stars were assigned based on level of significance as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test: ∗ = p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗ = p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗ = p ≤ 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗ = p ≤ 0.00001. Data from 3 biological replicate experiments and error bars represent mean ± SEM.